Imagine trying to build a house without a blueprint. Without clear plans, each worker might interpret the project differently—one starts with the roof, another with the walls, and someone else focuses on decorating before the foundation is even laid.
The result? Chaos, inefficiency, and wasted resources. Innovation in business works the same way. Without a clear definition of innovation, teams risk working in different directions, leading to misalignment, inefficiency, and missed opportunities.
Innovation is often used as a buzzword, as it can take many forms if not properly defined. For some companies, it’s about disrupting an entire industry, while others concentrate on continuous innovation to enhance efficiency. Some businesses prioritize technology-driven advancements, while others see innovation as a vehicle for solving societal challenges. Without a clear, company-specific definition, innovation can become unfocused, making it harder to measure success or allocate resources effectively.
For innovation to succeed, businesses need to connect it to their goals, whether it’s developing new revenue streams, sustaining continuous innovation, or gaining a superior market position. A clear definition ensures everyone—from leadership to frontline teams—understands what innovation contains and how it drives success.
In this article, we explore top companies innovation definitions and showcase real-world examples across five key innovation definition approaches: innovation by customer-centricity, disruption, process improvement, technology push, and social change. By understanding these different perspectives, businesses can develop their innovation mandate and bring it to life using the right formats and tools.
Meaning of innovation in business: The 11 innovation dimensions
Innovation is about developing new possibilities by introducing innovative concepts or improving existing products, processes, or services. It is not limited to technological breakthroughs but includes incremental innovations that enhance value, improve quality, or solve customer problems. At its core, innovation is finding better ways to address challenges and seize opportunities.
Any innovation can differ in the following dimensions:
-
How new? - Degree of innovativeness (incremental innovation vs radical innovation)
-
New for whom? - Scope of innovativeness (new to the firm, the industry, the world)
-
What is new? - Type of innovation (product, service, process, business model)
This variety causes a lack of a universal definition of innovation. Typically, innovation is seen as a new and applicable output. Yet, innovation can also refer to the fact that the ways to develop value are new. As such, the most common definition of innovation is:
An innovation is a new means-end combination where the means to develop value and/or the ends (the value delivered) itself are new and applied by an audience.
To be actionable for any company, companies need to define their innovation process and provide a more specific innovation definition to guide their innovation activities. By providing direction on what they innovate, for whom they innovate, how they innovate, and how new their innovations should be, companies ensure to use resources most effectively.
The innovation process is crucial for systematically fostering and implementing innovation, involving steps like identifying opportunities, generating ideas, and evaluating results. Without a clear innovation definition across the whole organization, efforts can lose traction, leading to wasted time and resources.
Effective innovation management plays a critical role in enhancing long-term competitiveness for organizations by establishing structured systems to manage both incremental and disruptive innovations. To drive impactful pay-offs and secure innovation adoption, it is essential to know what to innovate.
The following 11 innovation dimensions explain what to innovate. Organizations can either innovate single innovation dimensions or the complete innovation system.

Managing innovation comes with challenges, especially when balancing bold new ideas with continuous improvement. Many organizations struggle with scaling innovative solutions or shifting from traditional methods to more agile, cross-functional methods. A proper definition will help overcome these challenges.
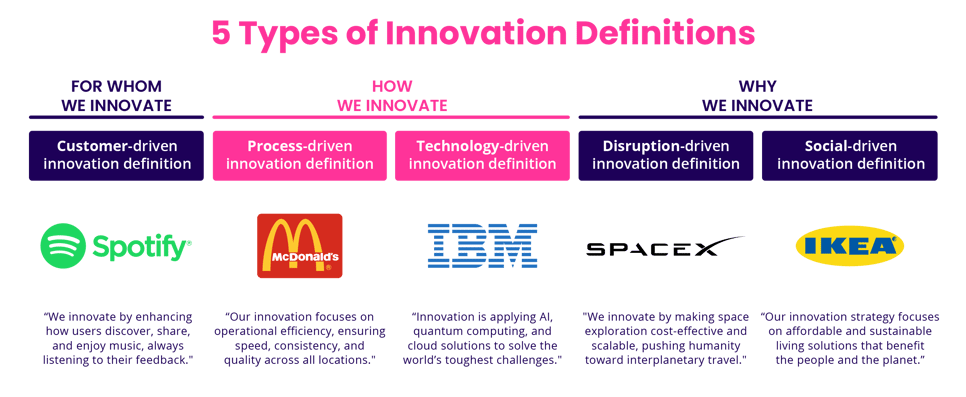
The 5 types of innovation definition for companies
Innovation means customer-centricity
Innovation means customer-centricity
Customer-centric innovation focuses on solving problems and creating value for customers. It starts with understanding their needs, preferences, and pain points, and then designing products, services, or experiences that enhance their lives. Companies like Amazon and Apple excel at this by continuously iterating based on customer feedback and anticipating future desires.
Service innovation is a form of customer-centric innovation that focuses on creating value through improved services.
This approach emphasizes empathy, where innovation stems directly from the voice of the customer, ensuring relevance and impact. It’s not just about developing something new but delivering solutions that resonate deeply with users, fostering loyalty, and driving sustainable business growth through meaningful connections.
Innovation means disruption
Innovation means disruption
Disruptive innovation challenges the status quo by fundamentally rethinking industries and developing entirely new ways of operating. It introduces breakthroughs that redefine markets, often rendering traditional methods obsolete. Companies like Tesla and Netflix exemplify this by revolutionizing sectors such as transportation and entertainment.
Innovation leading involves distinguishing between sustaining and disruptive innovations. Disruptive innovations can create new markets and displace established competitors, highlighting their importance for long-term business success and how foundational technologies can drive gradual changes in business models over time.
This type of innovation is bold and transformative, pushing boundaries to deliver new possibilities that competitors struggle to match. It often involves risk and requires companies to embrace change and adapt quickly. By disrupting existing systems, organizations can achieve a competitive advantage, redefine consumer expectations, and open up entirely new revenue streams.
Innovation means incremental innovation and process improvement
Innovation means incremental innovation and process improvement
Process improvement innovation focuses on optimizing internal operations to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality. It’s not about introducing groundbreaking technologies but making incremental changes that deliver significant value over time. Companies like Toyota and General Electric (GE) lead in this area by continuously refining their processes through methods like lean manufacturing and operational excellence.
Innovation processes play a crucial role in fostering a supportive innovation culture and improving productivity. By implementing appropriate tools and creating collaborative environments, organizations can drive continuous improvement and adapt to changing market demands.
This approach ensures smoother workflows, minimizes waste, and improves resource allocation, enabling organizations to adapt to market demands more effectively. By prioritizing continuous improvement, companies can build a strong foundation for growth, sustain their competitive edge, and deliver better outcomes for both customers and stakeholders.
Innovation means technological innovation push
Innovation means technological innovation push
Technology push innovation is driven by advancements in science and engineering, creating new products or solutions that shape industries. Companies like Google and IBM excel in this by leveraging cutting-edge technologies like AI, cloud computing, and quantum computing to solve complex problems and open new possibilities.
This type of innovation emphasizes proactive development, where new technologies lead the way, even before market demand fully materializes. It requires significant R&D investment and the ability to foresee how emerging technologies can transform industries. By adopting a technology push strategy, firms can achieve breakthroughs, gain a competitive advantage, and set future trends.
Innovation means social change
Innovation means social change
Social change innovation focuses on addressing societal and environmental challenges to create a more sustainable and equitable future. Companies like Patagonia and Unilever lead the way by rethinking their products and processes to reduce environmental impact and promote social well-being.
This type of innovation goes beyond profits, prioritizing long-term solutions that align with ethical and sustainable values. It includes efforts like reducing waste, improving energy efficiency, and fostering inclusion. By driving social change, organizations not only contribute to a better world but also strengthen their brand reputation and build trust with socially conscious consumers.
20 examples of how companies define and apply innovation
Companies characterize innovation based on their industry, strategy, and goals—some focus on customer experience, others on market disruption, process optimization, or technology advancements. Some also use innovation to drive sustainability and social impact.
Below are 20 real-world examples of how companies apply innovation across five key approaches: customer-centricity, disruption, process improvement, technology push, and social change. These examples illustrate how businesses embed innovation into their strategy, helping others refine their innovation mandate.

5 examples of customer-driven innovation definitions
Customer-driven innovation concentrates on understanding and solving customer needs to deliver better experiences and create value. Many leading companies define their innovation efforts through this lens:
Amazon: "Innovation starts with the customer and works backward to create solutions that simplify and enhance their lives."
Apple: "We innovate by imagining what customers will need next, even before they realize it themselves."
Nike: "Our innovation aims to solve problems for athletes, pushing the boundaries of performance."
Procter & Gamble (P&G): "Innovation is about improving lives by creating superior products that address real consumer needs."
Spotify: "We innovate by enhancing how users discover, share, and enjoy music, always listening to their feedback."
These companies prioritize the voice of the user to guide their innovation strategies, ensuring relevance, satisfaction, and long-term loyalty. By focusing on customer needs, they consistently deliver impactful, market-leading innovations.
Practical implications of customer-driven innovation definitions
Customer-driven innovation requires open feedback portals, real-time insights, and pattern detection tools to stay ahead of customer trends and evolving market requirements. Companies must use rapid prototyping and user testing to identify pain points in the customer journey and refine solutions.
Cross-functional collaboration ensures seamless execution, turning insights into impactful innovations. Companies that embrace this approach gain a competitive advantage, boost customer loyalty, and drive sustainable growth by consistently addressing real-world needs.
/Videos/HiFi-Animation-Ideation-Dynamic-Collaboration.png?width=1200&height=720&name=HiFi-Animation-Ideation-Dynamic-Collaboration.png)
5 examples of disruptive innovation definitions
Disruptive innovation challenges traditional business models, reshaping industries by introducing new, more efficient ways of delivering value. Many leading companies define their innovation efforts through this approach:
Tesla: "We innovate by rethinking industries from first principles, developing sustainable energy solutions that challenge conventional norms."
Netflix: "Innovation is about constant reinvention—anticipating shifts in consumer behavior and transforming entertainment through technology."
Uber: "We challenge outdated systems, creating a flexible, on-demand transportation model that redefines mobility."
Airbnb: "Our innovation reimagines travel by enabling people to share spaces, offering unique and authentic hospitality experiences."
SpaceX: "We innovate by making space exploration cost-effective and scalable, pushing humanity toward interplanetary travel."
These companies thrive by questioning industry norms, taking bold risks, and leveraging technology to disrupt markets. Their innovation strategies concentrate on scalability, efficiency, and redefining consumer expectations, allowing them to transform entire industries and develop new economic opportunities.
Practical implications of disruptive innovation definitions
Disruptive innovation requires bold risk-taking, rapid scalability, and a willingness to challenge industry norms. Companies embracing this approach must invest in emerging technologies, agile business models, and continuous experimentation. Success depends on identifying market gaps and redefining consumer expectations.
However, disruption also brings challenges, including regulatory hurdles and resistance from incumbents. Strategically, organizations must widely scan their horizon and centralize insights by using a technology radar.

5 examples of process-driven innovation definitions
Process-driven innovation centers on optimizing efficiency, reducing waste, and improving workflows to enhance firm performance. Many leading companies understand innovation through constant change and operational excellence:
Toyota: "Innovation is a relentless commitment to continuous innovation in every process, ensuring quality, efficiency, and sustainability."
General Electric (GE): "We drive industrial transformation by refining operations, adopting lean principles, and enhancing productivity."
Siemens: "Innovation is integrating domain expertise with digital solutions to optimize complex industrial processes."
3M: "We innovate by transforming scientific discoveries into practical, scalable solutions that improve everyday life."
McDonald's: "Our innovation focuses on operational efficiency, ensuring speed, consistency, and quality across all locations."
These companies prioritize incremental innovation, automation, and process optimization to maintain competitiveness. By refining workflows and leveraging data-driven decision-making, they improve cost-effectiveness and adaptability. This approach allows organizations to scale efficiently, enhance customer satisfaction, and remain resilient in rapidly evolving markets.
Practical implications of process-driven innovation definitions
Process-driven innovation enhances efficiency, cost reduction, and operational consistency, enabling companies to scale effectively. Companies must invest in automation, lean methodologies, and open innovation to optimize workflows.
This approach reduces waste and improves productivity but requires strong change management and continuous monitoring.
Strategically, process innovation ensures clear processes that scale easily from idea to product. Kanban boards help steer bringing the right improvements to production.

5 examples of technological innovation definitions
Technological innovation concentrates on leveraging advancements in science, engineering, and digital transformation to develop new solutions. Many leading companies define their innovation strategy through a technology-first approach:
Google: "Innovation is the freedom to experiment, fail, and learn—pushing AI, cloud computing, and automation forward."
Microsoft: "We innovate by empowering individuals and organizations through cutting-edge technology and digital transformation."
IBM: "Innovation is applying AI, quantum computing, and cloud solutions to solve the world’s toughest challenges."
Intel: "We push the limits of computing power to enable the next generation of technological breakthroughs."
Samsung: "Our innovation strategy is built on developing advanced technologies that redefine connectivity, mobility, and smart living."
These companies center on research and development (R&D), automation, and emerging technologies to maintain an advantage. By driving AI, cloud computing, and digital offerings, they shape the future of industries, improve efficiency, and unlock new possibilities that transform how people and companies operate.
Practical implications of technological innovation definitions
Technological innovation drives efficiency, scalability, and competitive superiority by integrating AI, automation, and digital transformation.
Companies must invest in a strong R&D portfolio, emerging technologies, and continuous experimentation to stay ahead. While this approach fosters breakthrough solutions, it requires high investment, skilled talent, and adaptability to rapid change.
Strategically, organizations must balance innovation speed with market readiness, ensuring new technologies solve real problems while maintaining long-term sustainability, cybersecurity, and regulatory compliance in an evolving digital landscape.
5 examples of social innovation definitions
Social innovation refers to addressing societal and environmental challenges by integrating sustaining innovations with inclusivity and ethical practices. Many companies define their innovation efforts through a social impact lens:
Patagonia: "Innovation means rethinking how products are made to reduce environmental harm and drive sustainable change."
Unilever: "We innovate by creating sustainable solutions that improve health, reduce waste, and drive responsible business growth."
IKEA: "Our innovation strategy focuses on affordable and sustainable living solutions that benefit people and the planet."
Schneider Electric: "We develop innovative energy solutions that increase efficiency while promoting sustainability and accessibility."
Danone: "Innovation is about improving global health and nutrition through responsible sourcing and sustainable food production."
These companies prioritize sustaining innovations, ethical sourcing, and social responsibility, proving that innovation can drive both organizational success and positive societal impact. By addressing environmental and social challenges, they build trust, long-term resilience, and stronger relationships with consumers and stakeholders.
Practical implications of social innovation definitions
Social innovation requires companies to integrate sustainability, ethical sourcing, and social responsibility into their operations. Companies must invest in eco-friendly materials, circular economy models, and fair labor practices to meet consumer expectations.
While this approach strengthens brand trust and long-term resilience, it demands regulatory compliance, transparency, and sustainable supply chain management. Strategically, organizations must balance profitability with social impact, ensuring that innovation aligns with both company objectives and global sustainability goals.
How to support innovation initiatives with a fitting definition
Innovation is not a one-size-fits-all concept. Companies define and approach innovation differently depending on their goals, industries, and market needs. Let’s compare the five primary approaches: Customer-Centricity, Disruption, Process enhancement, Technology Push, and Social Change—highlighting their pros, cons, and relevance.

Innovation as customer-centricity
This approach prioritizes solving consumer problems and enhancing experiences. It relies heavily on feedback, user insights, and tailoring solutions to meet market needs.
Support innovation plays a crucial role in developing environments that foster customer-centric innovation through appropriate tools and strategies.
-
Pros: Builds customer loyalty, ensures relevance, and fosters sustainable growth by aligning directly with consumer demands.
-
Cons: Risk of over-relying on existing customer feedback, potentially missing disruptive opportunities or visionary innovation.
Customer-centricity works best in competitive industries where market satisfaction and retention are critical, such as retail and services.
Innovation as disruption
Disruptive innovation transforms industries by introducing entirely new ways of operating. It challenges traditional business models and often reshapes consumer behavior, providing significant economic advantages by achieving a competitive edge through innovation.
-
Pros: Develops new markets, achieves market advantage, and drives exponential growth.
-
Cons: Requires significant risk-taking, high investment, and can alienate existing customers or partners.
This approach is ideal for tech-driven industries or companies looking to pioneer revolutionary change.
Innovation as process improvement
Process innovation concentrates on improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and streamlining workflows.
-
Pros: Enhances profitability, reduces waste, and ensures sustainability in the long term.
-
Cons: May lack the excitement or competitive edge of customer-focused or disruptive innovations.
This approach suits industries with high operational complexity, such as manufacturing or logistics.
Innovation as technology push
Technology push innovation introduces solutions driven by advancements in engineering and science, often before the market recognizes a need. Supporting innovation through government policies, funding for research and development, and the establishment of innovation agencies creates environments that foster technological advancements.
-
Pros: Sets trends, leads markets, and opens up untapped opportunities.
-
Cons: High R&D costs and risks, potential misalignment with market readiness or customer needs.
This approach is most effective in industries like IT, healthcare, and energy, where new technologies often redefine possibilities.
Innovation as social change
Social change innovation addresses environmental and societal challenges, aligning business goals with ethical and sustainable values.
-
Pros: Builds trust, enhances brand reputation, and resonates with socially conscious consumers.
-
Cons: Requires balancing profitability with long-term sustainability goals, which can be challenging for some companies.
This approach is gaining importance in industries like fashion, food, and consumer goods, where sustainability and ethical practices are key differentiators.
How to develop your innovation definition
Developing an innovation definition—or innovation mandate—starts with aligning it to your company’s goals, market position, and resources. A well-defined mandate ensures clarity and concentration for your innovation efforts, helping you support innovation initiatives and achieve meaningful outcomes.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Align with strategy: Your innovation definition should directly support your company’s mission and vision. For instance, if your strategy prioritizes customer retention, a customer-centric approach is ideal. On the other hand, if you aim to leapfrog competitors, a disruptive innovation strategy may be more suitable.
Understand your industry: Different industries demand different innovation approaches. In manufacturing, process improvement is often key to boosting efficiency and cutting costs, while in technology, a technology push approach is critical to staying ahead of trends. Analyze industry benchmarks and competitors to see what works and identify gaps your company can address.
Engage stakeholders across the organization: Innovation isn’t just for R&D or leadership—it requires input from all levels. Include customer insights, frontline employee feedback, and leadership vision to shape an innovation mandate that resonates.
Assess resources and capabilities: Not all innovation approaches are feasible for every company. A technology push strategy requires substantial R&D investment, while a social change focus demands strong sustainability expertise and partnerships. Be realistic about what your company can achieve and ensure resources are allocated accordingly.
Find the right balance: Many successful companies blend approaches. For instance, Tesla combines disruption and technology push, while Unilever merges social change with process improvement. Consider integrating multiple approaches to diversify your innovation portfolio.
Stay adaptive: Innovation needs to evolve with market demands and your company’s growth. Regularly revisit your innovation definition to ensure it remains relevant and aligned with changing priorities.
By incorporating insights from industry leaders and your company’s unique context, your innovation mandate will serve as a roadmap for driving impactful, sustainable growth.
Ultimately, the right approach balances ambition with practicality, ensuring your innovation efforts drive both short-term wins and long-term value. By crafting a clear innovation mandate, businesses can focus their efforts, foster collaboration, and ensure meaningful outcomes.
Bring your innovation definition to life, in the ITONICS Innovation OS
A sound innovation definition is just the first step—bringing it to life requires structured processes, collaboration, and the right tools. The ITONICS Innovation OS provides a centralized platform to turn your innovation definition into action, ensuring alignment across teams and driving measurable outcomes.
With trend and technology scouting, you can continuously track market requirements, customer trends, and disruptive forces that shape your industry. The platform enables real-time collaboration, ensuring that data-driven insights and strategic priorities guide innovation management.

Use ITONICS Ideation to collect, evaluate, and prioritize ideas based on your innovation mandate, ensuring that the best concepts move forward. With customizable roadmaps and portfolio management tools, you can align projects with your business model, resources, and long-term goals.
By leveraging ITONICS, organizations can streamline innovation workflows, foster transparency, and execute their innovation strategy with confidence—transforming ideas into real-world impact.











