Communication and dissemination of innovation building blocks and, subsequently, innovation strategy and objectives is an integral part of the end2end innovation journey. It increases visibility, transparency, and collaboration and should continuously draw attention to the What, Why, and How of innovation projects.
By raising awareness and eliciting proactive responses from teams, strategic and unified communication can help create more agile, strategically aligned businesses.
What is dissemination?
The intentional communication of strategic objectives to all stakeholders.
The Foresight and Strategy phase of innovation requires processing information to anticipate, prepare for, and shape possible futures effectively. Processing happens by evaluating the scope, potential impact, and time to market for each Trend and Emerging Technology and analyzing interrelations between Trends and Emerging Technologies. Evaluation and analyses activities require collaboration and organization-wide expert input.
Engaging and involving the right people along this journey is essential for success. The Dissemination process ensures that relevant stakeholders get the right information and have a platform to share their expert views that enhance the innovation journey. The Foresight and Strategy activities might be owned by an innovation, research, or business modeling team, but Foresight is not only an expert topic. In some cases, it is necessary to include a larger group of internal and external stakeholder views.
Dissemination happens at various stages during the Foresight and Strategy process. The democratization of this process allows employees to be involved and have the opportunity to influence some decision-making through collaborative efforts. For acceptance and integration of innovation objectives, employees and stakeholders must understand the process, methodology, and opportunity spaces. Disseminating the information in appropriate ways invites awareness, confidence, and participation in achieving innovation goals.
What role does dissemination play within the end-to-end innovation journey?
Organizations that wish to innovate often invest resources into technologies and training but, in many cases, neglect internal communication as part of the innovation journey. This can be costly as developing ideas and processes requires collaborative input as a means of stress testing. In addition, organization-wide commitment is needed to ensure the necessary resilience to carry out innovation projects. Using the Dissemination process ensures buy-in and dedication for innovation journeys from all stakeholders. It is important to remember that the innovation process is a collaborative undertaking. Involving team members creates the understanding, confidence, and individual investment needed to achieve innovation goals.
Innovation feeds on interaction, information, and collaboration, and leveraging the power of two-way conversations yields reliable results during the Foresight and Strategy phase. Shifting practices of 'information pushing' to 'information sharing' and eventually 'knowledge exchange' allows for integrated participation and the production of enriched knowledge.
As part of the Foresight and Strategy phase, Dissemination across an organization helps:
- Strategic alignment by ensuring that the organization’s structure, resources, and culture support the strategy.
- Facilitate knowledge transfer by sharing internal expertise and innovation intelligence.
- Catalyze commitment by securing buy-in and engagement across the organization.
- Democratize innovation by empowering everyone to innovate.
How to work with the 3 pillars of dissemination
Disseminating environmental scanning information as part of the Foresight and Strategy phase aims to inform and involve internal, and in some cases, external stakeholders. Communications during this phase should consider not only employing the pillars of Dissemination but should also consider the characteristics of the correspondence.
How do I communicate innovation objectives and activities throughout the organization?
 |
 |
 |
| Accuracy | Specificity | Reliability |
| Accuracy refers to the clarity of innovation objectives, activities, and timelines and the assurance that stakeholders receive the right information at the right stage of the innovation process. |
Specificity refers to the degree of detail contained within the strategic goals that shape innovation activities and the control objectives by which they are measured. Specificity should allow for easily accessible and digestible information. | Reliability refers to the integrity of information made available to stakeholders, backed by credible data and disseminated through a trusted and established communication structure. |
Having accurate, specific, and reliable communication ensures an organization-wide view on the topics that affect the business today and shares the vision on how to deal with these changes for tomorrow. The vision of appropriately responding to changes is developed based on collaborative input and knowledge exchange using reliable tools and techniques.
It is harnessing team members' different expertise and perspectives and channeling these efforts to identify problems and opportunities that result in rigorous and sustainable innovation objectives. Once innovation objectives are identified, it is equally essential to Disseminate the innovation intentions throughout the organization. It is crucial that employees are able to answer the question: ‘What difference will this make if we are successful?’
Successful Dissemination throughout all Foresight and Strategy phases relies on the following pillars:
1. The identification of key stakeholders
Decide who needs to be included at the various stages of the innovation journey. This entails identifying individuals or departments with certain areas of expertise and capabilities to leverage. Have a clearly defined objective for why you are communicating specific information with the respective groups—i.e., are you trying to raise awareness or alignment, secure buy-in and commitment, or call for concrete solutions or actions?
The goal here is to understand each stakeholder according to their willingness to participate and their influence based on expertise and decision-making powers. Using concepts from the Stakeholder Influence Importance Matrix may assist you in:
- Mapping stakeholder groups and prioritizing communications
- Deciding on proper dissemination approaches
- Identifying what objectives you would like each group to attain
- Determining what action accompanies each objective
The Stakeholder Influence Importance Matrix activity will yield different results during the Foresight and Strategy phase stages. It is crucial to continuously evaluate active stakeholders and accompanying actions, depending on which stage the process is in.
2. The development of a common language
Ensure that when communicating an innovation strategy or socializing a particular Trend or Technology, you do so in simple language that people in all departments can understand. Language can connect, but complex jargon can alienate. Using conventional language to disseminate Environmental Scanning information and Foresight and Strategy Objectives saves time and eliminates room for confusion and misinterpretation.
Organizations often compartmentalize language according to business units or expertise. However, using common language helps to democratize the innovation process by allowing everybody to be involved actively. Consider saying everything that is necessary, but not being overly embellished in the language or descriptions. Ask yourself whether you are either diluting the message or using unnecessary elaborations to get your message across.
3. The establishment of a single point of truth
While there are several ways to disseminate information, having a flexible, digital tool for company-wide communication and collaboration raises innovation intelligence and, ultimately, action. Using a single point of truth will help:
- Avoid miscommunication
- Save time
- Reduce stress and increase appetite for collaboration
- Keep everyone interested and engaged
- Build trust in the process
- Create transparency across the organization
Tools for facilitating successful dissemination
Disseminating information and creating platforms for knowledge exchange may happen using a variety of tools and techniques. Trend and emerging technology reports can assist in communicating significant developments, and similarly, internal reports created by innovation departments can play a valuable part in circulating information.
Internal newsletters can also be used to strategically communicate specific information to particular stakeholder groups as identified using the 3 pillars of Dissemination. Newsletters can highlight the latest Trends, Emerging Technologies, and Inspirations, or this method may indicate actions required from certain team members. Internal communication channels can also be used; however, too many channels quickly become problematic as information is dispersed and can get lost in many organizations.
Using a digital collaboration tool as a single point of truth enables effective and efficient dissemination of information and allows succinct and purposeful knowledge exchange.
How ITONICS acts as a single point of truth for effective dissemination in innovation:
|
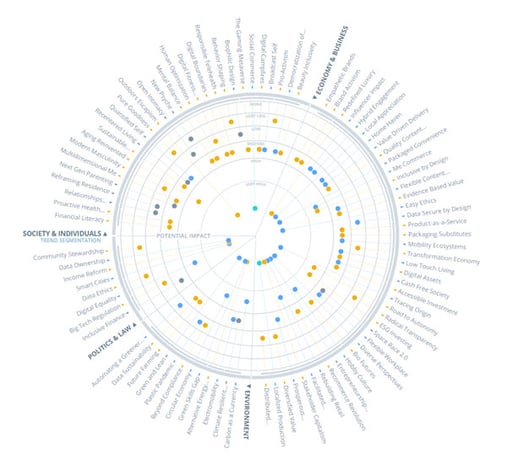
Use the ITONICS Radar to communicate important Trends and Emerging Technology information that can be easily configured to demonstrate Scope, Time to Market, Potential Impact, Business Relevance, Strategic Fit, Need for Action, Complexity, and Attractiveness. This will help communicate important principle constituent information for your innovation strategy. |
|
|
|
|
|
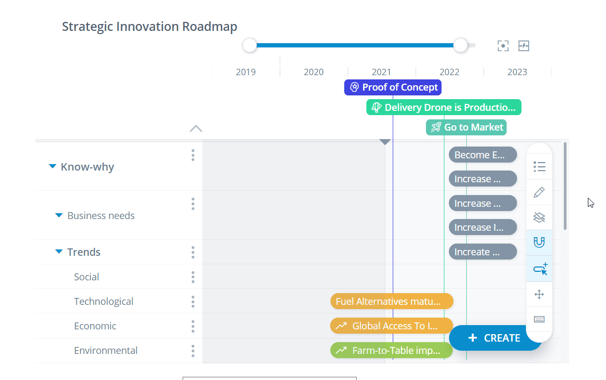
The ITONICS Roadmap enables easy ways to plan and keep track of your innovation projects across multiple users or teams within dynamic environments on the software. Easily view internal milestones and add connections that indicate the impact of other projects and/or developments on milestones and timelines. |
|
|
 |
|
|
ITONICS Solutions are able to integrate various data sources that allow for consolidated and up-to-date monitoring and management of innovation processes. It allows for easy communication that speaks to decision-makers in various positions in the company and integrates knowledge from inside and outside the company. |