Understanding trends and emerging technologies is essential to discover growth opportunities in your industry. While all trends and emerging technologies are important, some are more relevant than others.
Why emerging technologies and trends matter for business strategy
Preparing for the future requires organizations to carefully consider Where to Play, How to Win, and What to Execute. To identify Where to Play successfully, business leaders must understand both the opportunities and potential threats posed by emerging technologies, new legislation, and shifting customer expectations.
Decision-makers and innovation architects know that a firm understanding of emerging and changing environments is the foundation of future-fit adjustments. But with vast amounts of information feeding into the business environment today, how do teams identify relevant trends that drive competitive advantage through innovation?
How to move from environmental scanning to sensemaking
Environmental Scanning systematically searches for signals of change, which can be recognized from a wide variety of sources. This process is fundamental to identifying where your organization needs to position its purpose, process, product, and people for the highest impact. However, to move from scanning weak signals to detecting meaningful data clusters—the early indicators of emerging trends—teams must apply evaluation methods grounded in both qualitative and quantitative analysis.
At ITONICS, we view trends as demand drivers that indicate market pull; they guide innovators in knowing what consumers need and desire. Demand drivers help innovators better understand market and consumer shifts.
We define emerging technologies as solution drivers that represent a market push. They provide disruptive, game-changing solutions to problems faced in the market.
In the ITONICS Innovation OS you will find a curated collection of nearly 170 emerging technologies and trends, along with thousands of real-world examples of innovation. These drivers of change and what we call “inspirations” are researched, evaluated, and packaged by our team of analysts. This content is supplemented by various thematic presets and preconfigured radars in ITONICS. And it can serve as a foundation to help you kickstart monitoring your business environment.
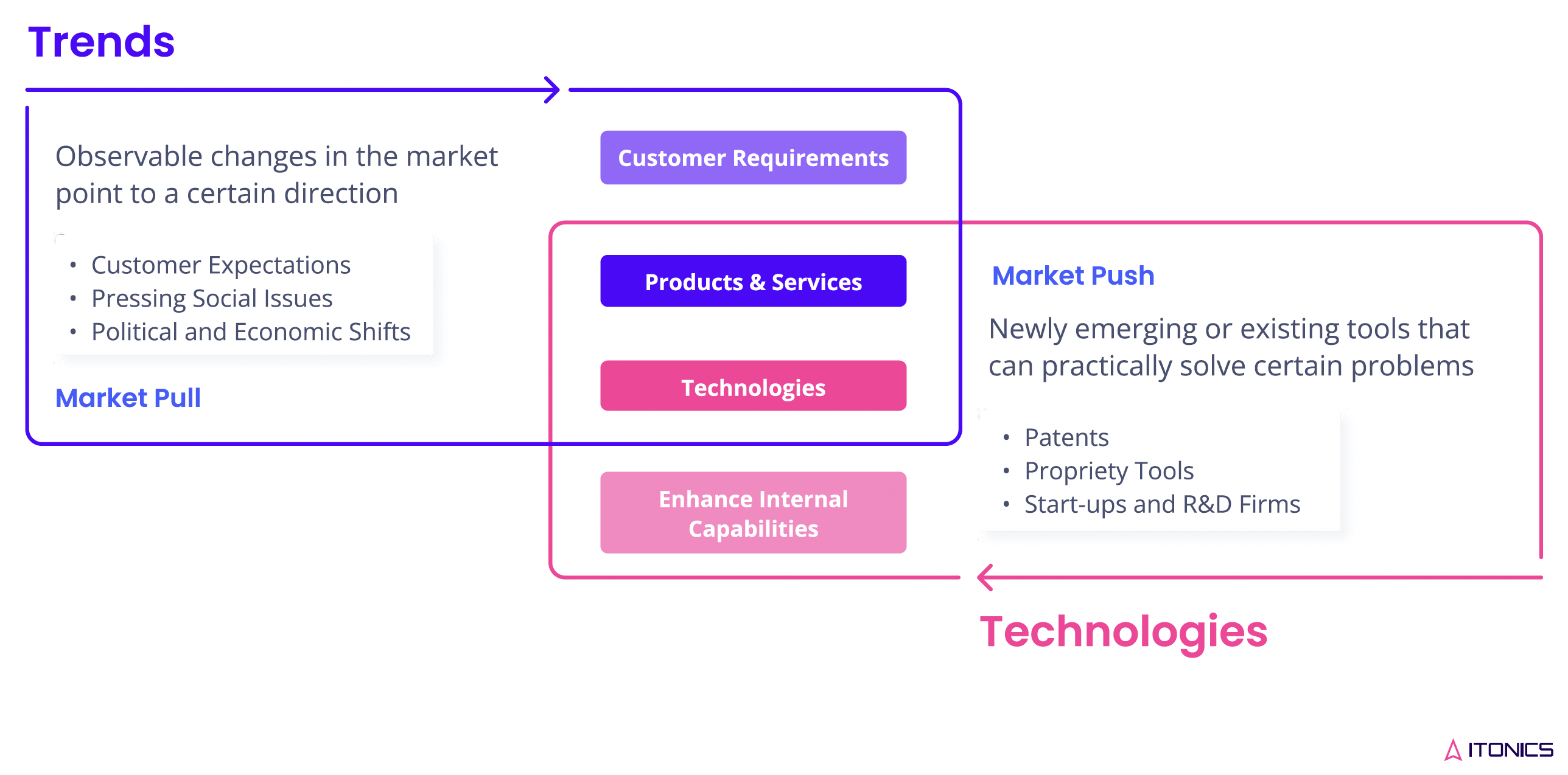
Exhibit 1: Trends and technologies as driver of change
Evaluation and quantifying processes are necessary to help teams identify the most relevant directions of change. Relevancy must consider external factors as well as respective organizational variables. Applying a rating and evaluation system to these variables should include both qualitative and quantitative data points alongside collaborative inter-division expertise to yield the most robust results.
What are trend and technology ratings
Rating tools may be used to assess weak signals, inspirations, or clusters of data that indicate a trend. Rating criteria can similarly be used to rank emerging technologies against relevance and prominence within an industry or for a particular organization.
Using review and rating tools that incorporate both quantitative and qualitative data as well as internal organizational knowledge assists teams in guarding against internal biases. Quantitative and qualitative rating criteria also ensure that trends and technologies are ranked and evaluated consistently and from a holistic perspective.
Trends and technologies may share some of the same rating criteria. Although, due to their differing forces on the market (i.e., trends = pull; technologies = push), it may be necessary to consider their ratings separately. A trend gains its relevance from measuring how pervasive and impactful its influence has become. While a technology is evaluated by its complexity and how far it has been developed.
Ratings have to consider predefined data sets, and organizations must decide which criteria to use when evaluating. This might include geography, industry penetration , sustainability impact, or time-to-market. Structured evaluations help organizations focus on what can truly transform industries and improve market share.
Consider who in the organization would be best suited to rate which criteria. Another way to consider rating roles is to identify who would be best suited to rate at which stage of the sensemaking process.
How to use ITONICS ratings to identify relevant trends and emerging technologies
Each trend and emerging technology in the ITONICS Showroom is presented with ratings that indicate penetration, scope, and adoption metrics (Exhibit 2). Understanding what these ratings mean and how they are derived helps organizations focus their attention and identify Where to Play.
Our analyst team uses advanced queries and the ITONICS Insights tool to collect relevant information from quantifiable historical and present data. This is supported by qualitative research to statistically derive the ratings.
ITONICS has assigned ratings based on the following predefined criteria:
Trends:
- Scope
- Potential Impact
- Time to Market Impact
- Adoption Stage
Emerging technologies:
- Scope
- Potential Impact
- Complexity
- Technology Readiness Level (TRL)
- Technology Attractiveness
Discover how ITONICS derives these ratings:

Exhibit 2: Trend and technology rating criteria
How to use internal ratings to evaluate emerging trends and technologies
Teams can best understand what each trend and emerging technology might mean for their business by conducting an internal exercise to collaboratively evaluate each element based on unique industry- and company-specific parameters.
ITONICS has provided the following internal rating criteria for organizations to consider:
Trends:
- Business Relevance: How relevant is this element to your business?
- Strategic Fit: How well does this element fit into your organization’s overall strategy?
- Need for Action: How important is it that your organization take action with regard to this Element?
Emerging technologies:
- Internal Know-How: How much internal know-how does your business possess with regard to this element?
- Need for Action: How important is it that your organization take action with regard to this element?
The ratings above are pre-set in the ITONICS Showroom. However, organizations can tailor rating criteria to align with their own set of needs and workflows.
Different elements may also call for different types of rating criteria. For instance, teams can collaboratively evaluate their concepts, prototypes, solutions, or capabilities by setting up their own ratings.
Common rating criteria include:
|
Criterion |
Definition |
Possible Scale |
| Novelty | How novel is the idea? | New to Business Unit, New to Company, New to Business, New to Industry, New to World |
| Customer Demand | How pressing is the solution for customers? | Basic Improvement, Performance Improvement, Excitement Improvement (cf. Kano Model) |
| Customer Validation | How satisfied are the test users? | Analysis of survey results with customers |
| Cost-Benefit Ratio | How much benefit results out of the costs? | ROI: 0-1%, 1-2%, 3-5%, 6-10%, 11-20%, >20% |
| Team Strength | How capable is the team to bring the innovation to operation? | Very Limited to Very Strong wrt. required skills |
Internal evaluation of trends, emerging technologies, and other elements is vital for effective innovation management. When undertaken in the environmental scanning stage, it helps empower teams with the consensus needed to ensure strategic relevance, strengthen buy-in, and act decisively.
There are generally two approaches to attributing internal rating responsibilities: community and expert. The community approach invites all members of a group, typically all employees, to rate; this is often appropriate for idea evaluation based on general criteria. The expert approach limits rating to a dedicated group of people who apply their expertise in either a certain subject matter or in foresight strategy; this is often appropriate for trend or technology evaluation based on specific criteria.
Depending on the approach and objectives, the evaluation process can occur continuously or on a targeted basis. Organizations or teams can send invites or run workshops to collect targeted ratings for the purpose of annual or quarterly portfolio updates. This ensures organizations keep their environmental scanning activities aligned to their strategic goals.
Using Visual Tools to Identify Key Trends and Technologies
Being able to visually compare and filter emerging trends and innovative technologies enables organizations to focus their attention on the elements most relevant to their business strategy. By understanding what the ITONICS ratings convey and undertaking a process of internal rating, organizations can determine what variables and metrics to prioritize.
In the ITONICS software, trend and technology radars can then be set up with different views based on a specific rating criterion and scores. For instance, if an organization wants to view only those technologies that it has collaboratively rated with a high Need for Action, the radar can be set to this view. Additionally, users can save this view as a filter that can be shared and used for future decision-making.
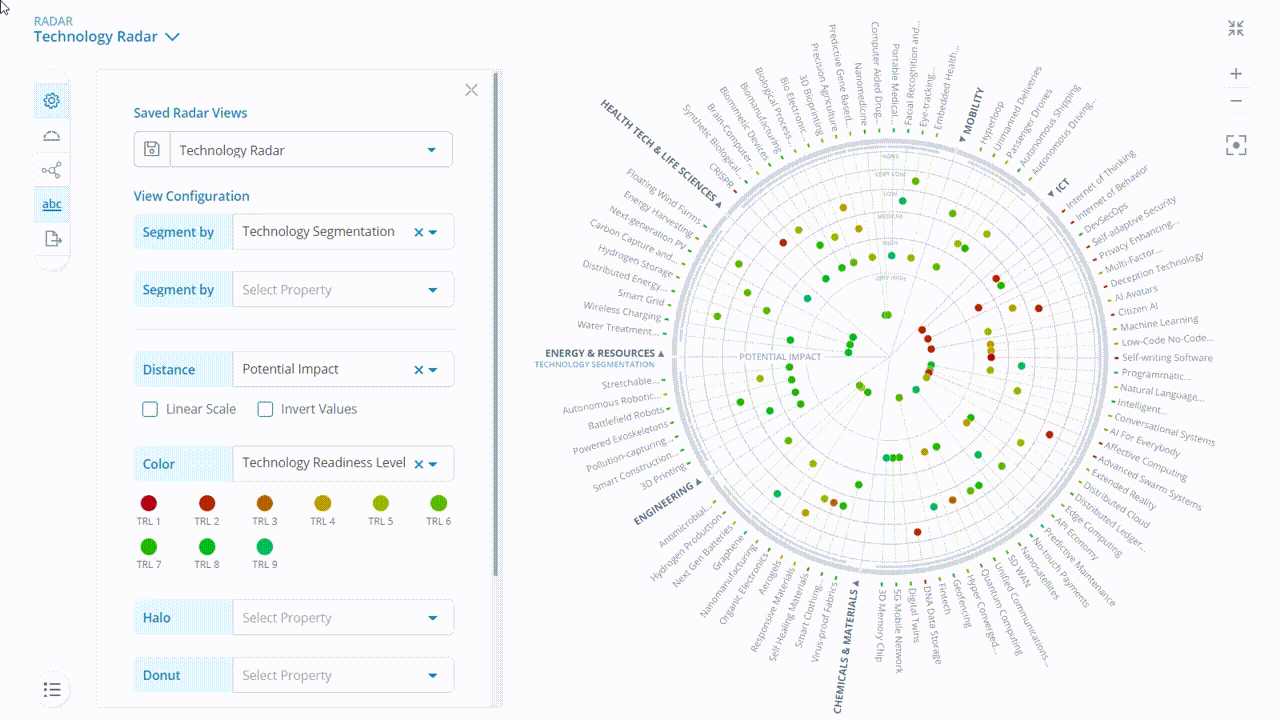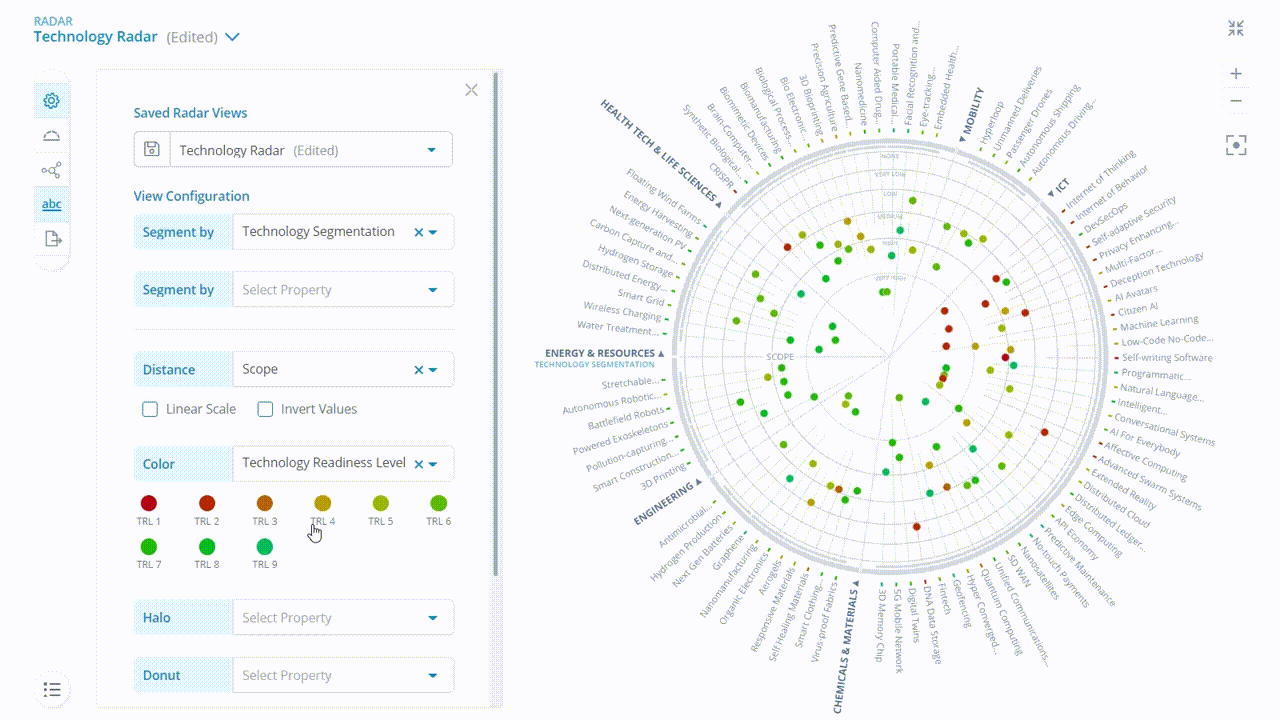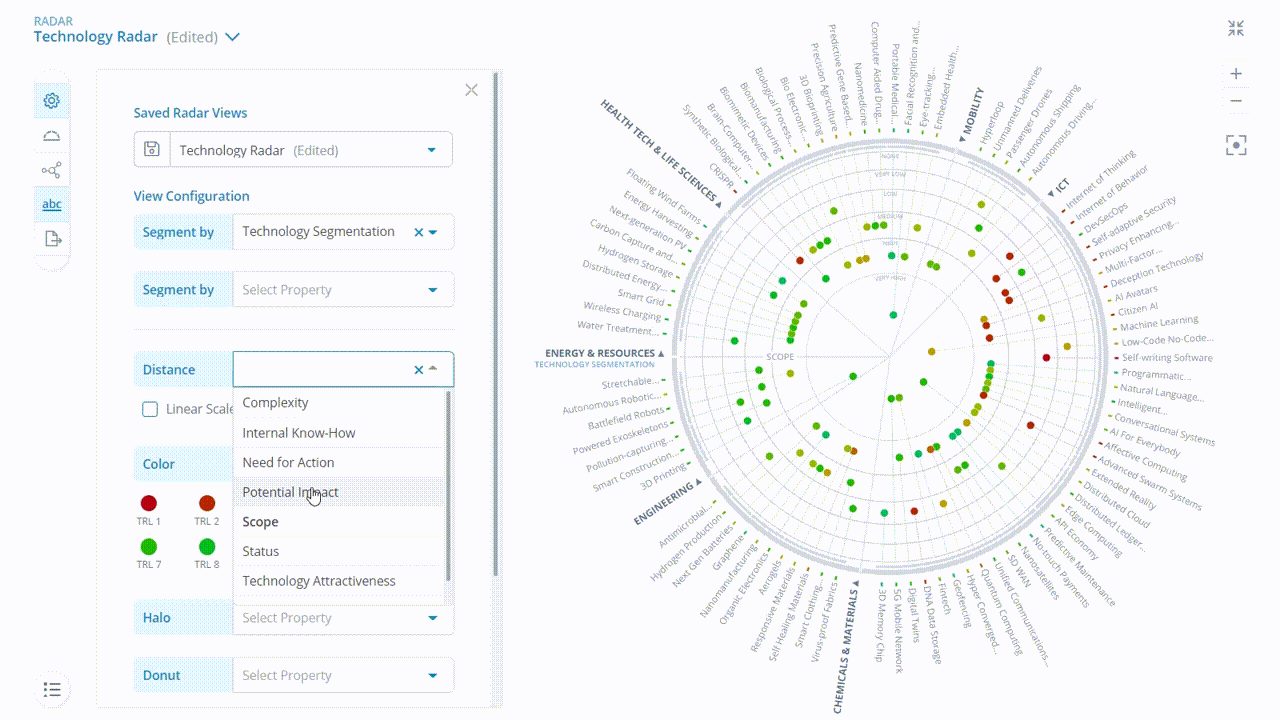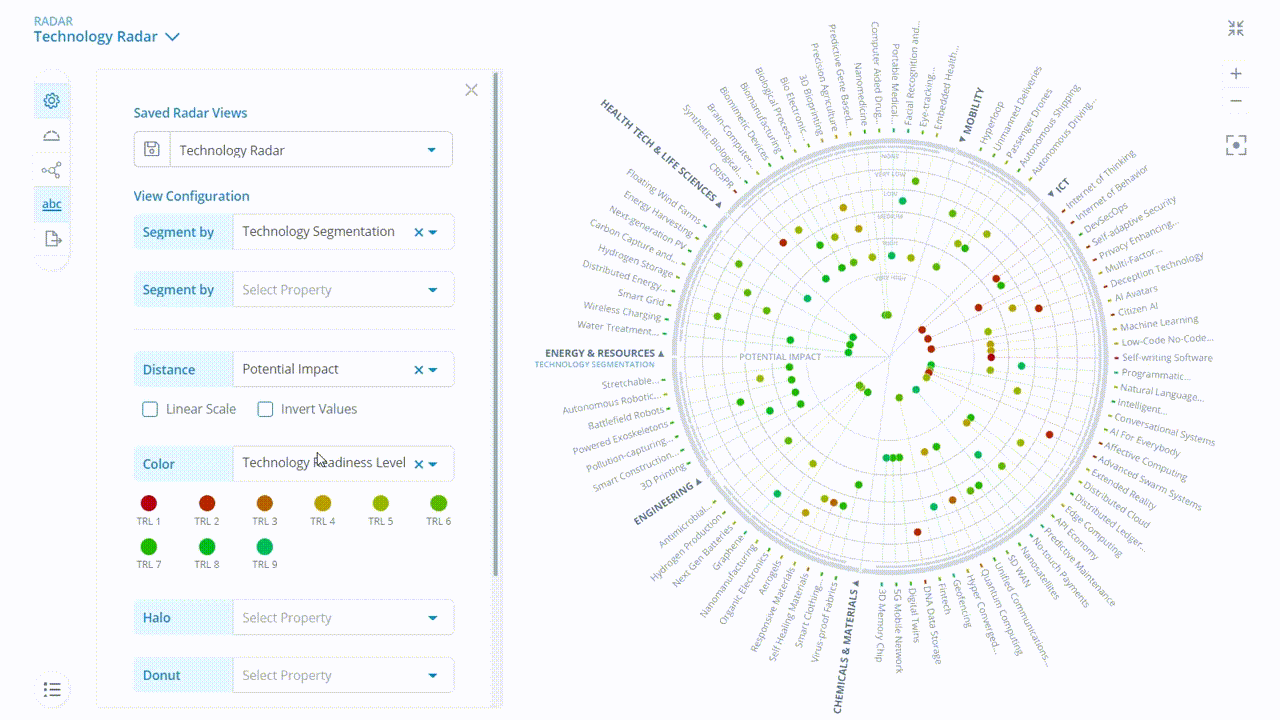
The interactive radar can visualize all elements based on their evaluation. This overview helps you to interpret your business situation and deduce possible next steps.
Also see:
Identify industry trends and emerging technologies with ITONICS
Ready to upgrade your trend and technology scouting process?
With ITONICS' powerful innovation management software, you'll not only have everything you need to streamline your company's innovation processes from end-to-end, but you’ll also have the tools you need to identify new business opportunities, collaborate with team members across departments, and share insights to foster alignment and purpose.
Book a free demo today to see the benefits and features of the ITONICS Innovation OS.
FAQs on identifying trends and technologies
What is the definition of technology trends in business?
Technology trends in business refer to emerging patterns, innovations, or developments in technology that have the potential to change how companies operate, compete, and grow. These trends can result in disruption and impact business strategy, customer engagement, and market dynamics.
Why is it important to identify emerging trends and technologies?
Identifying emerging trends and technologies helps organizations stay competitive, avoid potential threats, and seize new growth opportunities. It enables proactive decision making and informs innovation strategy.
How can I identify the most relevant trends for my organization?
Start with environmental scanning, then evaluate trends using qualitative and quantitative criteria such as business relevance, strategic fit, and urgency. Visualization tools like the ITONICS radar can help make sense of it all, and prioritize what matters.
What’s the difference between trends and emerging technologies?
Trends are demand-driven shifts in behavior or human needs (market pull), while emerging technologies are solution-driven innovations (market push) that address specific problems or create new capabilities.
What tools can support trend and technology scouting?
Innovation management platforms like ITONICS offer radar visualizations, rating systems, and collaborative workspaces to help teams monitor, evaluate, and act on the most important trends and technologies.
Which tools help identify disruptive trends and technologies?
Platforms like ITONICS enable organizations to identify disruptive trends and technologies through AI-powered environmental scanning, interactive radar visualizations, and collaborative evaluation workflows.





