Roadmaps act as the compass that steers companies toward success. Roadmaps provide control, security, and clear direction for single teams, departments, entire organizations, or even countries. Take Apple's or Tesla's roadmap examples – their product roadmaps have driven consistent innovation and market leadership by setting clear priorities and timelines for development.
Roadmaps break down complex goals into manageable steps, helping businesses avoid costly missteps and stay agile in the face of change. They bring clarity and alignment across teams and stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is working toward the same direction.
In short, a well-executed roadmap is the backbone of any plan and strategy, guiding every step from concept to execution to success.
/Still%20images/Foresight%20Mockups%202025/foresight-set-milestones-and-activities.webp?width=966&height=604&name=foresight-set-milestones-and-activities.webp)
Short answers and FAQs on roadmaps
What is a roadmap?
A roadmap is a visual planning tool that outlines a strategic plan over a defined timeline. It communicates goals, initiatives, milestones, and dependencies, helping teams stay aligned and track progress toward long-term objectives.
What is roadmapping?
Roadmapping is the process of creating a structured plan that outlines how an organization will achieve specific goals over time. It helps visualize the strategic direction, prioritize initiatives, and align teams across functions.
Why are roadmaps important?
Roadmaps are essential for aligning stakeholders, prioritizing efforts, and ensuring everyone understands the direction and timing of key initiatives. They turn high-level strategy into actionable steps and improve transparency across teams.
What types of roadmaps are there?
There are various types of roadmaps depending on their use case, including:
- Strategic roadmaps for long-term business planning
- Product roadmaps for feature development and releases
- Technology roadmaps for tracking emerging tech and capabilities
- Project roadmaps for managing timelines and resources
- Marketing and IT roadmaps for departmental planning
What should a roadmap include?
A roadmap typically includes:
- Clear objectives
- Timeframes or phases
- Key initiatives or deliverables
- Responsible owners or teams
- Dependencies and milestones
- Metrics or KPIs (optional)
How do you create a roadmap?
To create a roadmap:
- Define your goals and strategic priorities.
- Identify major initiatives or themes.
- Set a realistic timeline with milestones.
- Map dependencies and assign ownership.
- Choose the right format or tool (e.g., spreadsheet, software).
You can use free roadmap templates or dedicated software like ITONICS to streamline the process.
Are there tools or templates to help build a roadmap?
Absolutely. ITONICS offers free, customizable roadmap templates in Excel and PowerPoint formats to help you get started quickly with structured planning. For more advanced needs, the ITONICS Innovation OS provides powerful, collaborative roadmapping software. It allows teams to visualize strategic initiatives, align activities across departments, and adapt plans in real time—all in one centralized platform. Whether you're just starting out or scaling innovation across the organization, ITONICS gives you the tools to build smarter, more dynamic roadmaps.
Definition: What is a roadmap?
A roadmap is a time-based representation of a plan. It outlines the activities and milestones required to achieve specific goals or complete a project.
Serving as a visual guide, it illustrates the direction, priorities, and progress of an initiative over time, ensuring alignment with the organization's business goals. Roadmaps help, for instance, product teams stay aligned, make informed decisions, and communicate the overall vision to all stakeholders involved.
Whether launching a new product, embarking on a marketing campaign, or executing a company-wide transformation, a roadmap provides the framework to navigate the complexities of any initiative. You can also understand a company's roadmaps as a representation of its innovation strategy.
By presenting a clear picture of the path ahead, roadmaps enable teams to anticipate challenges, allocate resources effectively, and adjust plans as necessary. They are dynamic tools that evolve with the project, allowing for flexibility and adaptation in response to changing circumstances.
Benefits of roadmaps
The term "roadmap" in a business context draws from its literal meaning in navigation to represent a visual plan for reaching a destination. It gained popularity as industries became more complex, especially in technology and product management, where long-term planning and cross-functional coordination are critical.
The widespread diffusion of roadmaps as a management practice can be attributed to their ability to simplify complexity, improve alignment, and provide a clear, adaptable framework for decision-making. Companies increasingly adopt roadmaps because they offer a flexible yet structured way to manage evolving market demands, technological advancements, and internal teams, making them invaluable in guiding successful execution.
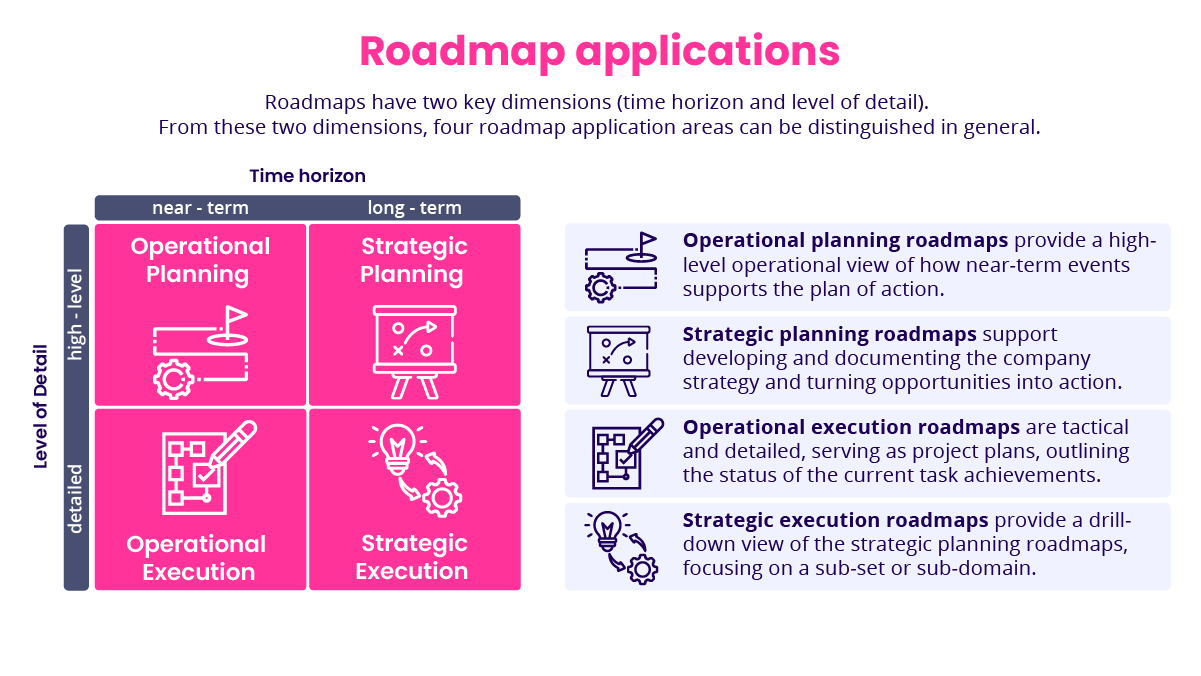
Overall, there are four major benefits:
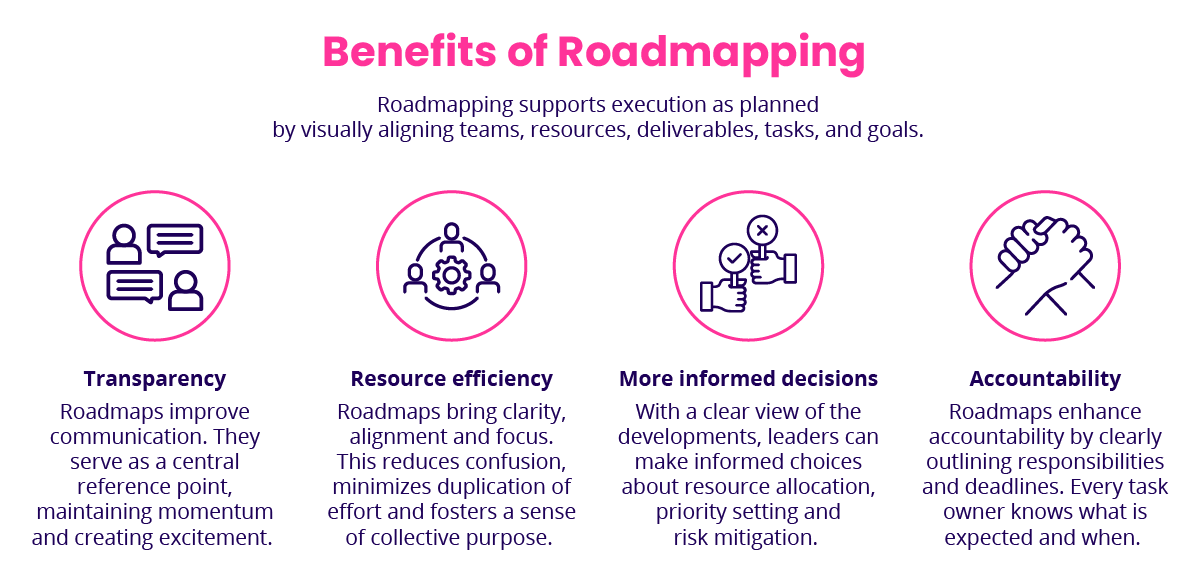
More efficient operations: Roadmaps bring clarity and focus to projects that might otherwise become overwhelming or disjointed. They align teams around shared objectives, ensuring that everyone understands the goals and the steps required to achieve them. This alignment reduces confusion, minimizes duplication of effort, and fosters a sense of collective purpose.
Increased accountability: Roadmaps enhance accountability by clearly outlining responsibilities and deadlines. Every task owner knows what is expected and when their contributions are due, helping keep the project on schedule. Stakeholders can monitor status, building trust and engagement. Roadmaps can also highlight customer benefits, showcasing how the product strategy will enhance sales efforts and directly benefit both sales representatives and their customers.
More informed decisions: With a clear view of the trajectory, leaders can make informed choices about resource allocation, priority setting, and risk management. Identifying potential bottlenecks early allows for adjustments to mitigate issues before they escalate.
Higher transparency: Roadmaps improve communication, acting as an internal reference or external conviction tool. They serve as a central source of truth that everyone can consult, reducing misunderstandings and ensuring that all parties are informed about the latest developments. This transparency is crucial for maintaining momentum and keeping the project on track.
Templates, examples, and owners of roadmaps
Understanding the different types of roadmaps can help you choose the template that best suits your needs. Different roles are responsible for creating and managing roadmaps, reflecting process differences between, for instance, product teams and other teams. In some cases, a master roadmap unites the individual roadmaps, showing the company’s big picture and strategy.
Product teams own product roadmaps
Product roadmaps focus on the definition of new products, features, and the evolution of a product. It explicates the product vision, and contains multiple products as well as customer feedback, and product ideas. Product roadmaps outline over time the deployment of new features, enhancements, and releases. Product roadmaps convey the product strategy.
Agile development influences the dynamic nature of product roadmaps. New urgent feature requests or serious customer complaints require a product roadmap to be kept flexible and responsive to changing market priorities. Product managers, developers, and stakeholders use these roadmaps to settle on what will be delivered and when.
The scenario which a software company uses a product roadmap to plan upcoming key releases is one of many typical product roadmap examples. By road mapping, they detail new functionalities, improvements, and release dates. This product roadmap guides engineering and informs marketing and sales colleagues.

Download the product roadmap template →
In new product development, product managers are typically responsible for the product roadmap - if it is not owned by the Chief Product Officer. A product manager creates the product roadmap. They maintain the product roadmap. The product roadmap should capture completely all prioritized customer needs, market trends, and business objectives. They coordinate with development, marketing, and sales teams to execute the plan. Product management plays a crucial role in creating an effective product roadmap by ensuring ongoing updates, controls, and information on product roadmap changes.
The time to build the product roadmap is when strategic planning is done. When leadership has set the strategic roadmap and themes, the exercise to create a roadmap can be the starting point for conversations about where to invest and how much. The best product managers create a strong product roadmap together with other stakeholders. As these stakeholders may have different interests, it is recommended to create multiple views and roadmap versions. Typically, updates to a product roadmap are made on at least quarterly basis.
Project managers own project roadmaps
A project roadmap is a timeline roadmap used to track tasks, assignments, and completion status compared to planned dates. These planned dates can be key milestones, deliverables, and deadlines. Project managers rely on these project roadmaps to coordinate tasks across different task owners. They ensure that the project stays on schedule. They also try to eliminate blockers as early as possible.
In larger organizations, the company roadmap may encompass multiple individual projects. Each of these projects can be managed with an individual project roadmap. This project roadmap is also called a Gantt chart. Yet, in a classical sense Gantt charts typically contain more detailed information than a project roadmap.

Download the project roadmap template →
An example could be a construction project initiative roadmap. The project management will create a plan that outlines initiatives such as design, permitting, foundation work, framing, and finishing. Each phase has its own set of tasks and timelines, allowing multiple teams to coordinate efforts efficiently.
Project managers (PMOs) own project roadmaps. They oversee the execution of tasks, manage timelines, allocate resources, and ensure that milestones are met. They act as the central point of contact for all project-related activities.
To create a project roadmap, it is necessary to create the project plan. Ensure you have a solid grasp of the project’s goals and clearly define what success looks like. While you create the entire project timeline, you should have a clear idea of the project’s scope, the tasks required to meet the objectives, and approximate start and finish dates. Once you understand the "why," "what," and "when" of the project, you can create the roadmap.
The roadmap for strategy teams
Strategic roadmaps or master roadmaps provide a high-level overview of an organization’s long-term goals and the strategies to achieve them. A well-defined product strategy informs their development. Leadership teams use them to align the company’s direction and make decisions about investments and initiatives.
For instance, a company aiming to expand internationally might create a timely plan outlining target markets, timelines for entry, resource requirements, and expected outcomes. This roadmap guides decision-making at the highest level and related to the most important business goals.
Typically, assistants to executive leaders or department heads take their ownership. To create this vision, you first need to define long-term goals, map activities to these goals, and allocate resources at the organizational level. In every steering committee meeting, they are used to guide company-wide initiatives and course corrections.

Download the strategy roadmap template →
Explaining a company strategy by a roadmap is a very efficient mechanism to commit employees to the company goals. This also explains why it is recommended to create such roadmaps at the end of the year for the next years. In a regular cadence, roadmaps need to be updated and controlled to ensure they have successfully executed roadmaps.
CTOs, CIOs, and technology roadmaps
Technology roadmaps, or IT roadmaps, map out the planned evolution of a company’s technological infrastructure. They map out the technology strategy and IT strategy. Development teams play a crucial role in executing these roadmaps by aligning with product groups to ensure successful project delivery and meet deadlines. Development teams help IT teams and decision-makers plan system upgrades, new technology adoptions, and integrations.
A technology roadmap might detail plans to migrate to cloud services, implement cybersecurity measures, or specific deadlines and important tasks. This confidential and internal roadmap ensures that technological advancements support the company’s strategic goals and operatability.
IT directors or Chief Technology Officers manage technology roadmaps. They plan technological advancements, system upgrades, and new implementations to support the company's strategic goals.
Download the technology roadmap template →
An organization planning a digital transformation could create a timeline roadmap detailing the migration to cloud services, adoption of artificial intelligence tools, and enhancement of cybersecurity measures. The roadmap helps coordinate IT initiatives with business objectives.
The guide to create a roadmap
To create a good roadmap, follow a logical sequence of eight steps. There are also roadmapping tools available that help you create your first roadmap.
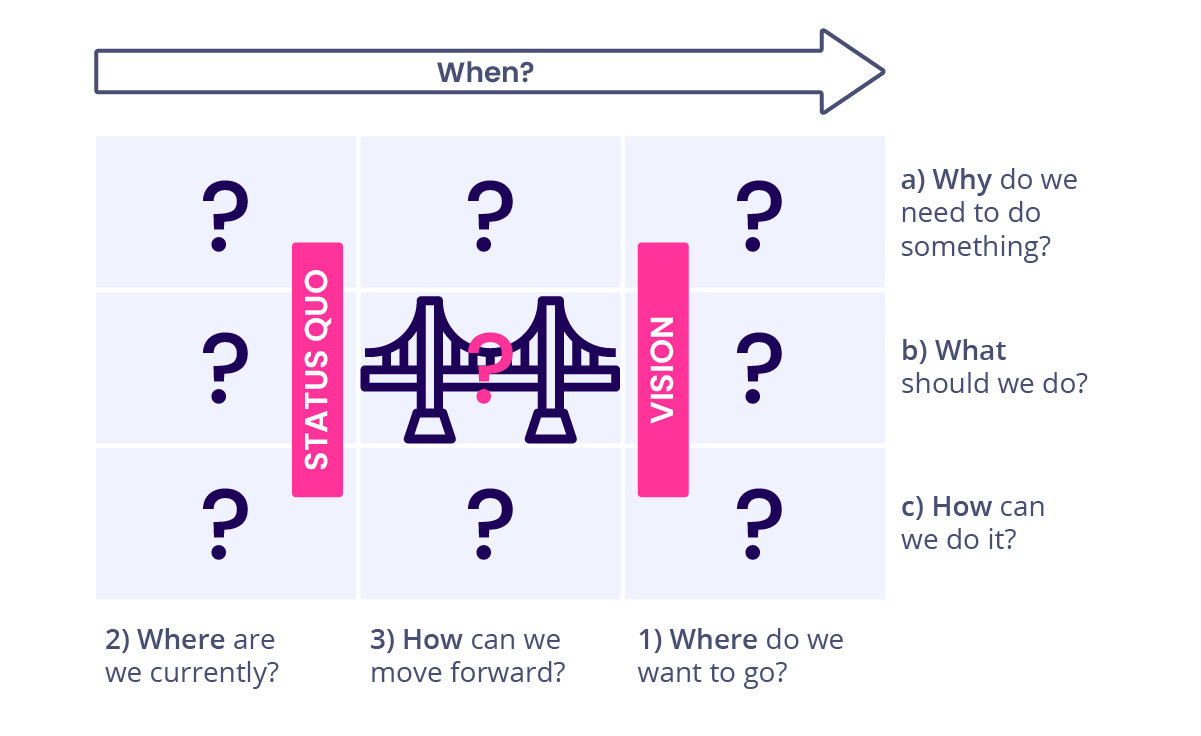
1. Create the roadmap structure and layers
Start by defining swimlanes and layers. What are the horizontal dimensions that form the background? Layers create a view of the domains you want to connect. For product roadmaps, think of different product teams, for instance. Each layer presents a workstream that can be managed individually and forms a comprehensive activity map in sum.
2. Set goals and key milestones
Across workstreams and over the roadmap’s time horizon, define goals and when they should be reached. Create global goals and team-specific goals to align them with the overall strategy. Ensure goals are SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Each goal represents a milestone—a deliverable expected at a certain time. A comparison of planned vs. achieved milestones indicates progress and helps keep the team motivated.
3. Outline tasks and activities
List the tasks and activities required to reach each milestone. First capture all necessary activities, then create a hierarchy: most important tasks first. With a roadmapping tool, you can place task deliverables in chronological order. By indicating expected start and end dates, you’ll see critical paths and can build a timeline roadmap.
4. Develop a realistic timeline
Estimate the time needed for each task and arrange them chronologically. Compare activities with milestones to set realistic expectations and avoid unattainable deadlines. Include buffers for unexpected delays or allocate more resources to critical deliverables.
5. Allocate resources
Determine what resources are needed for each task and ensure availability when required—people, budget, equipment, and external support. Resource planning prevents shortages that could hinder progress and makes the roadmap actionable. It also helps you track execution and course-correct.
6. Identify dependencies and risks
Map task and milestone dependencies and document key risks with owners and mitigations. This improves sequencing, avoids blockers, and raises issues early.
7. Communicate and maintain
Share the roadmap with relevant stakeholders using clear visuals and concise explanations. Encourage feedback and adjust based on input. A well-crafted presentation communicates strategy, goals, and themes to the right audiences.
Use visual and interactive versions to make complex information digestible and engaging. Host the roadmap on accessible intranet portals, ensuring the latest version is available to everyone.
Schedule periodic meetings or stand-ups to track progress, gather feedback, and reinforce alignment. Educate teams on goals and roles to build understanding and commitment.
Send regular email updates highlighting achievements, upcoming milestones, and changes. Tailor reports to executives, teams, and customers.
Consider an external roadmap for customers and prospects. Keep it appealing and easy to understand, focusing on high-level information about upcoming features and plans.
8. Monitor and update regularly
A roadmap is a living tool. Track progress, update it to reflect changes in customer needs and context, and communicate updates to the team. Bigger updates should happen annually and in sync with any strategy refresh.
Using roadmaps in different industries
Roadmaps are versatile tools used across industries, each adapting them to specific needs. Within each industry, terms and plans often map back to common roadmapping principles.
Product strategy and plans in the tech industry
In the tech sector, roadmaps are crucial for planning software product releases, software updates, and feature rollouts. Agile teams use roadmaps to coordinate sprint planning, manage backlogs, and align development with user feedback.
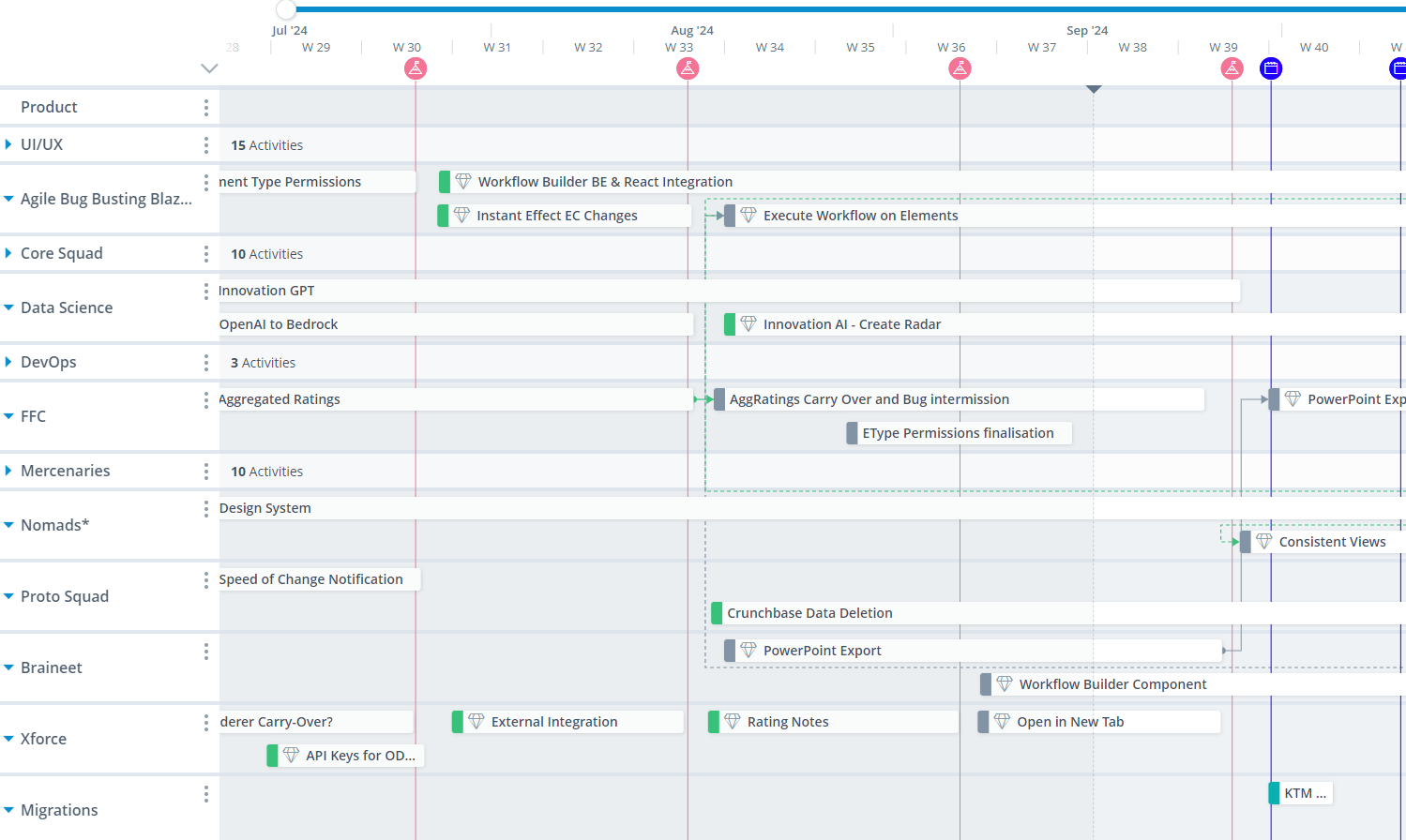
Roadmap creation is a collaborative process led by the product management team, ensuring alignment with the organization’s product strategy and involving all stakeholders to maintain clarity and focus. Sprint plans often focus on a time frame of 3 weeks. This is a more operational version of a roadmap.
Healthcare industry
Healthcare organizations use roadmaps to manage clinical development and integrated new product development plans, or a market access strategy and patient engagement plans. These roadmaps help coordinate across departments like IT, patient services, and administration.
Manufacturing industry
Manufacturers use roadmaps for product development, supply chain optimization, process improvements, and an innovation roadmap. They coordinate efforts across engineering, production, and logistics teams to enhance efficiency and quality.
Defense industry
Defense organizations use roadmaps to manage capability plans, integrated acquisition strategies, and technology readiness assessments. They coordinate efforts across divisions like procurement, research and development, and logistics to ensure alignment with national security objectives.
Specific terms like Joint Capability Integration and Development System (JCIDS), Defense Acquisition Lifecycle, and Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) are used to plan and execute programs efficiently. These roadmaps help synchronize activities across the Army, Navy, Air Force, and other agencies, facilitating collaboration on projects like weapon systems, force modernization, and mission readiness.
Finance industry
Financial institutions use roadmaps to create new financial products, digital transformation initiatives, and regulatory compliance strategies. They coordinate efforts across departments like risk management, IT, customer service, and compliance to achieve strategic objectives.
Specific terms such as Digital Transformation Roadmap, Regulatory Compliance Plan, Product Innovation Strategy, and Customer Experience Enhancement Program are commonly used to plan and execute projects effectively. These roadmaps help coordinate various teams to implement new technologies like mobile banking apps, adopt fintech solutions, ensure compliance with regulations like Basel III or GDPR, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) industry
FMCG companies use roadmaps to manage product development cycles, market expansion plans, and supply chain optimization strategies. They coordinate efforts across departments like marketing, production, sales, and distribution to quickly respond to consumer demands and market trends.
Specific terms such as Go-to-Market Strategy, Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), Demand Forecasting, Category Management, and Trade Promotion Planning are commonly used to plan and execute programs effectively. These roadmaps help coordinate teams to launch new products, optimize shelf placement, manage inventory levels, and strengthen retailer partnerships, ensuring products reach consumers efficiently and remain competitive in fast-paced markets.
How roadmap software eases and improves roadmapping
Creating and managing roadmaps manually can be complex and time-consuming. Roadmap software simplifies this with specialized tools for planning, collaboration, and execution.

By leveraging ITONICS Roadmap Software, organizations can significantly ease the process of creating and managing roadmaps. The software’s comprehensive features enhance collaboration, improve efficiency, and support strategic alignment, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes.
ITONICS Roadmap Software offers a robust platform that integrates all aspects of strategic planning and innovation management. With ITONICS, organizations can:
-
Streamline planning: Customizable templates and drag-and-drop functionality make it easy to map projects, set milestones, and assign tasks without extensive training.
-
Improve collaboration: Real-time updates and shared workspaces keep everyone aligned, reducing miscommunication and fostering teamwork.
-
Enhance visualization: Interactive timelines and heat maps present complex information accessibly, aiding stakeholder engagement and decisions.
-
Integrate data and insights: Integrations and trend/technology data align roadmaps with market developments and strategic objectives.
-
Increase agility: Quickly adjust the roadmap as projects evolve to respond to changes in environment or scope.
-
Ensure alignment with strategy: Strategic foresight and portfolio management features help keep initiatives tied to long-term goals.


