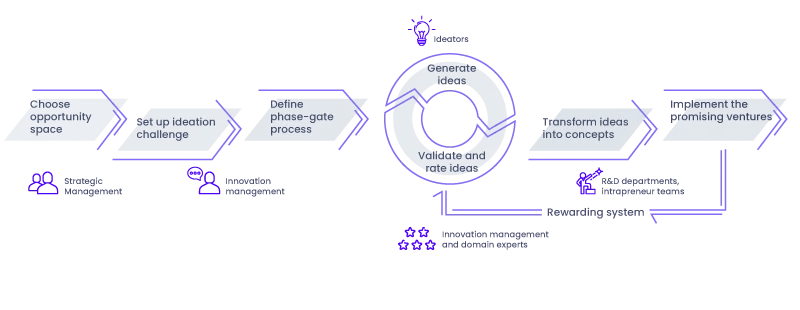
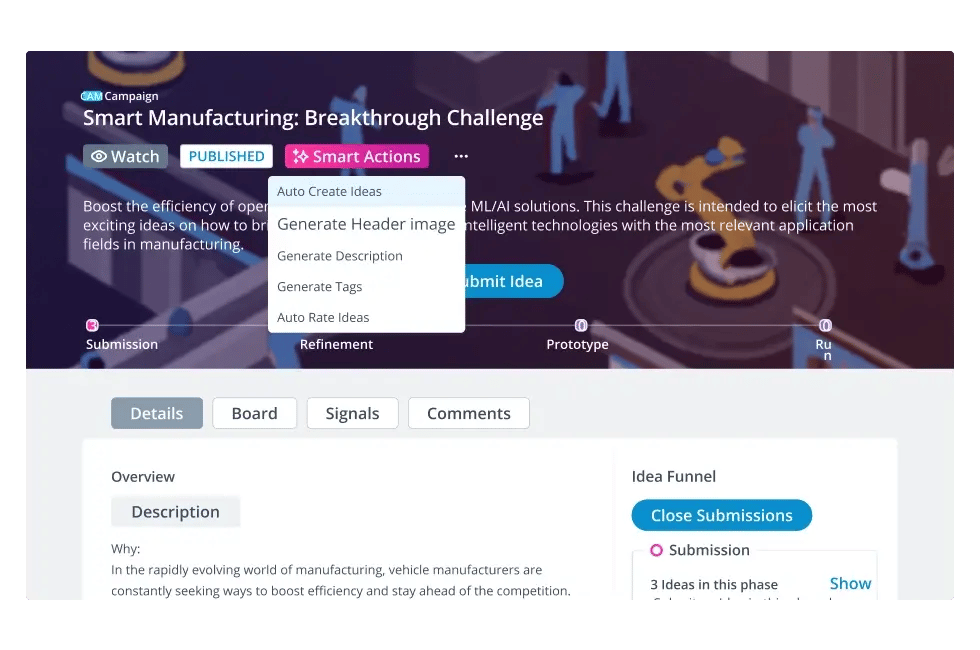
Why is ideation important in the innovation process?
Generating ideas in collaboration with employees, clients and partners helps to identify and create new products, services, and business models, and harnessing the creative potential of a crowd can be crucial to success. Usually, ideas are explored in answer to a specific question, or as a solution to a certain problem. Often, the ideas generated are based on the wishes or expectations for a product. Involving clients in the ideation process can provide valuable information that results in more robust ideation. By integrating users directly into product development, this information can be gathered better and faster than through conventional methods such as market research or trend scouting, which can result in improved product-market fit solutions.
The key benefits of generating ideas collaboratively are as follows:
- Enable goal-oriented ideation by connecting targeted ideation campaigns to previously identified growth opportunities that are aligned to strategic priorities
- Enrich the ideation process with creativity and external knowledge to spot relevant trends, technologies, and inspirations
- Engage global communities from small teams of experts up to global innovation networks
- Get instant feedback on innovative ideas and concepts from your target group in real-time
- Sustain the motivation by incentive systems, competitions, and gamification
- Set up KPIs, innovation governance, and innovation controlling schemes to maintain focus and ensure resource investments are well managed
- Create an entrepreneurial mindset and innovation culture across your organization
- Strengthen cross-functional collaboration
To ensure that your organization takes advantage of these benefits and maintains world-class ideation, the following challenges must be considered:
- Connecting ideation activities with business opportunities contributing to the overall company strategy
- Creating a collaborative ideation process that connects environmental scanning capabilities with innovation execution
- Selecting and implementing engagement and reward models
- Activating and maintaining the ideation community
- Choosing evaluation methods and criteria
- KPIs, innovation governance, and controlling
Different ideation methods
Ideation finds various fields of application in today's innovation context. As highlighted before, ideas can be generated, for example, at the corporate level with employees, external stakeholders like clients and partners, or from an unknown external crowd. This can happen in a contest setting or in ideation workshops. In this chapter, we will dive deeper into five different approaches to idea generation:
- Closed vs. Open Innovation (Crowdsourcing)
- Design Thinking
- Ideation Workshop
- Ideation Challenge
- Idea Portfolio
Also see: 10 Powerful Ideation Techniques to Unleash Creativity and Innovation
Closed vs. open innovation (crowdsourcing)
Closed innovation
Within the innovation process, you can differentiate between open and closed innovation. Closed innovation describes the conventional approach that innovation is developed exclusively within the company itself. This includes the generation of ideas for products, services, or business models, to concept creation and development.
Open innovation/ crowdsourcing
In order to increase the innovation capabilities within the company and create competitive advantages, opening up the conventional innovation process beyond internal boundaries and integrating the innovation potential of external stakeholders has proven to be a promising approach within the past decade. This is referred to as open innovation. By sourcing knowledge externally, organizations can counteract market uncertainties and the complexity of innovation and knowledge recombination. Open innovation involves a wide range of external actors, including users, customers, suppliers, universities, startups, and competitors. A variety of formats exist for accessing external knowledge, such as competitions and campaigns, corporate venture capital, or open-source platforms.
Generating innovative ideas and solution approaches by an external crowd, usually in the context of an innovation contest, is called crowdsourcing. The crowd can consist of either just a few experts or thousands of ideators. In this way, a broad mass of individuals with a wide range of characteristics and qualifications can be reached and their diverse potential used. To engage and motivate the crowd, the best ideas submitted are rewarded.
Design thinking
Design thinking describes a process for developing new concepts. It is often associated with creative facilitation, but the discipline is much more than creative workshops. It refers to user-centered methods for guiding innovation and an innovation framework that allows non-designers to approach problems like designers. Thanks to its open, flexible, and human-centered nature, design thinking became a popular method for driving innovation. The design thinking process consists of five steps: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test.
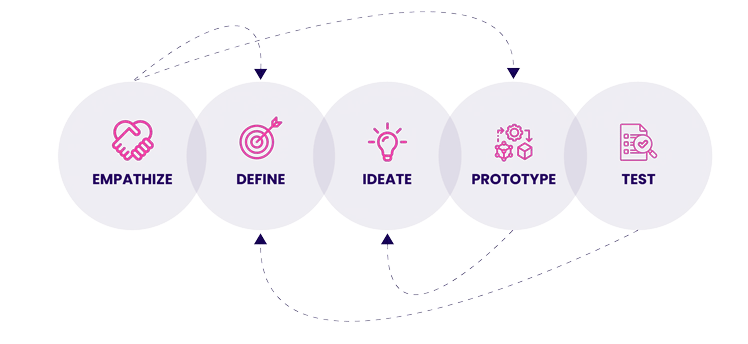
After understanding users' existing problems and defining their needs in the first two steps, the ideation phase involves developing ideas for potential solutions to fix the problem. There are a variety of ideation techniques that can be applied here, such as brainstorming or the Crazy 8’s method. Monitoring trends can be another helpful starting point, as they indicate consumer needs and demands based on observed changes in behavior.
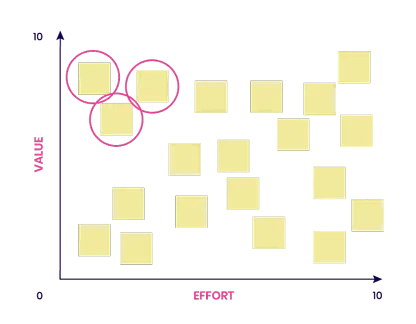
After generating a set of ideas, they are usually prioritized (e.g. in idea portfolios) before the most promising one is prototyped (MVPs - minimum viable products or mockups) and tested with users. This process helps innovators to identify at an early stage of the innovation process whether a product idea has value for users or not.