Developing a new product without a systematic process is like building a house without a blueprint—chaotic and risky. Without a clear plan, product development teams may pursue promising ideas, but without coordination, resources get spread thin, leading to delays, higher costs, and products that fall short of market needs. Projects often lose momentum before reaching completion.
A lack of structure also means missed feedback and poor market alignment. Without integrating customer insight and thorough market research, products can fail to resonate with consumers. This slows development, allowing competitors to take the lead while teams scramble to catch up. A structured new development process provides the blueprint needed to bring the right products to market efficiently (Exhibit 1).
/Still%20images/Portfolio%20Mockups%202025/portfolio-link-projects-teams-and-milestones-2025.webp?width=966&height=604&name=portfolio-link-projects-teams-and-milestones-2025.webp)
Exhibit 1: Systematic new product development plan
New product development (NPD) definition
New product development (NPD) is the process of transforming market needs into ideas and market-ready products. This new product entails a certain degree of newness allowing businesses to exploit market opportunities, respond to emerging trends, and increase customer satisfaction through thorough business analysis, which assesses product viability and strategizes marketing efforts. This process is essential for companies looking to maintain relevance and achieve business growth.
A structured new product development process follows clear stages, from feedback to market research analysis, idea generation, and commercialization. Each phase aims to shape the product concept into a product-market fit. That is why NPD ideas must align with user needs and customer wishes. This approach minimizes risks and increases the likelihood of a successful launch.
One of the main advantages of an organized NPD process is its ability to foster innovation. By moving through structured steps, companies can assess the viability of new ideas and allocate resources efficiently. This helps maintain focus and streamlines decision-making. It saves both time and money, and increases reputation in the target market and market share.
The key phases in the NPD process include opportunity exploration from customer feedback and market research, customer problem-fitting idea generation, technical solution feasibility validation, market-fit creating iteration, business model viability definition, and solution scaling.
These stages help filter out weak concepts and fine-tune promising ones. Every stage aims to ensure the product resonates with the target market's needs before a full-scale and costly implementation.
Benefits of a systematic new product development process
A systematic new product development (NPD) process offers key benefits that drive success (Exhibit 2).
One major benefit is risk reduction. By following structured steps, companies can identify potential challenges early and address them before full-scale product development. This minimizes costly errors and increases the likelihood of a successful product launch.
Efficient resource allocation is another advantage. A systematic approach helps teams allocate time, budget, and activities where they’re most needed. This focused use of resources ensures higher returns on investment and avoids wasted efforts on unviable ideas.

Exhibit 2: Benefits of a structured NPD process
Improved market alignment is also crucial. A well-organized NPD process includes market research and customer feedback integration. This ensures that new products meet customer needs, leading to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Lastly, a structured NPD process enhances collaboration. Cross-functional teamwork between marketing, design, and production teams fosters better communication and speeds up development. This alignment keeps everyone on the same page, streamlining the path from concept to market.
The best NPD process stages
The new product development (NPD) process is a structured sequence of stages that guide companies from initial ideas to a successful product launch. Each phase is designed to ensure that products are developed with minimal risk and maximum alignment to market needs.
Opportunity Exploration
This stage begins with identifying potential opportunities through customer feedback and market research. Companies gather insights on consumer preferences, industry trends, and pain points. Key decision criteria at this stage involve determining if the opportunity aligns with company goals and market potential. If it does, the idea progresses to the next phase. The idea screening process then evaluates each idea based on market potential, technical feasibility, and alignment with business goals, ensuring that resources are allocated to ideas with the highest chance of success.
Idea Generation
In this phase, the focus is on generating ideas that fit the identified customer problems. Brainstorming sessions, design thinking workshops, and collaborative meetings often take place here. The main decision criterion is whether the idea can effectively solve the target problem while aligning with customer needs. Only those that show strong potential for addressing real issues advance. Concept development is a critical stage where detailed versions of ideas are created and validated through testing.
Solution Feasibility Validation
This stage tests the technical feasibility of the proposed idea. Companies conduct prototyping, testing, and technical analyses to evaluate if the concept can be developed within current technological capabilities. The decision criteria involve assessing technical risks, cost feasibility, and the potential for successful implementation. Ideas that pass this validation move forward. A minimum viable product (MVP) is often used at this stage as a simplified version of the product to test essential features and gather market response.
Iteration
At this stage, the product undergoes iterations to align with market expectations. Feedback loops, pilot programs, and user testing refine the product’s features. The main criterion here is whether the product’s value proposition resonates with the target audience and addresses their needs effectively. Products that prove a strong market fit proceed to business modeling. Concept testing is a crucial step where customer feedback is gathered to evaluate the viability of product ideas.
Business Model Definition
Defining the business model ensures the product is financially viable. This phase includes cost analysis, revenue projections, and resource allocation planning. The decision criteria involve evaluating the product's potential profitability and sustainability. If the business case is sound, the product moves toward scaling.
Solution Scaling
In this final stage, companies focus on scaling the solution for full market launch. This involves finalizing production, marketing strategies, and distribution channels. The decision to move forward is based on readiness for mass production, marketing alignment, and potential scalability. Test marketing is a crucial stage where businesses gather customer feedback and research data to validate their marketing strategies and refine their launch messaging.
The best new product development process examples
For instance, Apple follows an intensive NPD process that starts with deep market exploration and user-focused design. Each stage, from prototyping to final product testing, involves stringent quality checks. This helps ensure that only well-vetted products reach the market.
P&G uses its “Connect + Develop” model for NPD. This includes opportunity exploration through partnerships and customer insights, followed by iterative development and feasibility validation. P&G’s method showcases a blend of external collaboration and strong internal processes to refine products effectively.
Tesla adopts an agile NPD approach that emphasizes rapid prototyping and real-world testing. Each stage is data-driven, using feedback from actual users to tweak product features. Tesla’s iterative process helps validate market fit and maintain continuous improvement.
These examples underline that a strong, systematic NPD process—marked by clear decision criteria at each stage—allows companies to develop products that align with market needs and succeed in competitive landscapes.
NPD process example 1: Horizon 3 NPD process
A horizon 3 innovation process aims for innovation that goes beyond the current core. It is the horizon of transformative and radical innovation. We saw the following innovation process with VNTR—the innovation and venturing unit at PostFinance.
Anchoring its decision-making in strategic foresight, VNTR begins the innovation process by identifying and exploring relevant signals, trends, and technologies. This foresight phase aims to derive new fields of innovation that may hold potential new opportunities for PostFinance.
The validation phase bridges strategic foresight with operational scalability. It involves rapid market experiments to test feasibility and customer needs. Defined hypotheses are rigorously verified or falsified, ensuring a smooth transition from ideation to operation. Validated hypotheses propel projects toward the final phase.
VNTR's final phase focuses on efficiently scaling initiatives for sustained growth, within or beyond the organization. It entails implementing validated innovations, optimizing processes, and adapting strategies for long-term success in dynamic markets.
VNTR rigorously evaluates every innovation project through a phase-gate process—not all emerge successfully. At each gate, and continually based on evolving insights, decisions are made: to proceed with enthusiasm (love it), refine as needed (change it), or discontinue (leave it) with informed judgment.
Twice yearly, VNTR hosts a collaborative workshop to define new innovation fields using trends and insights. Opportunities emerging from this session are presented at Gate 0, defining upcoming topics for exploration and steering VNTR's future actions.
NPD process example 2: 360° Insight Collection
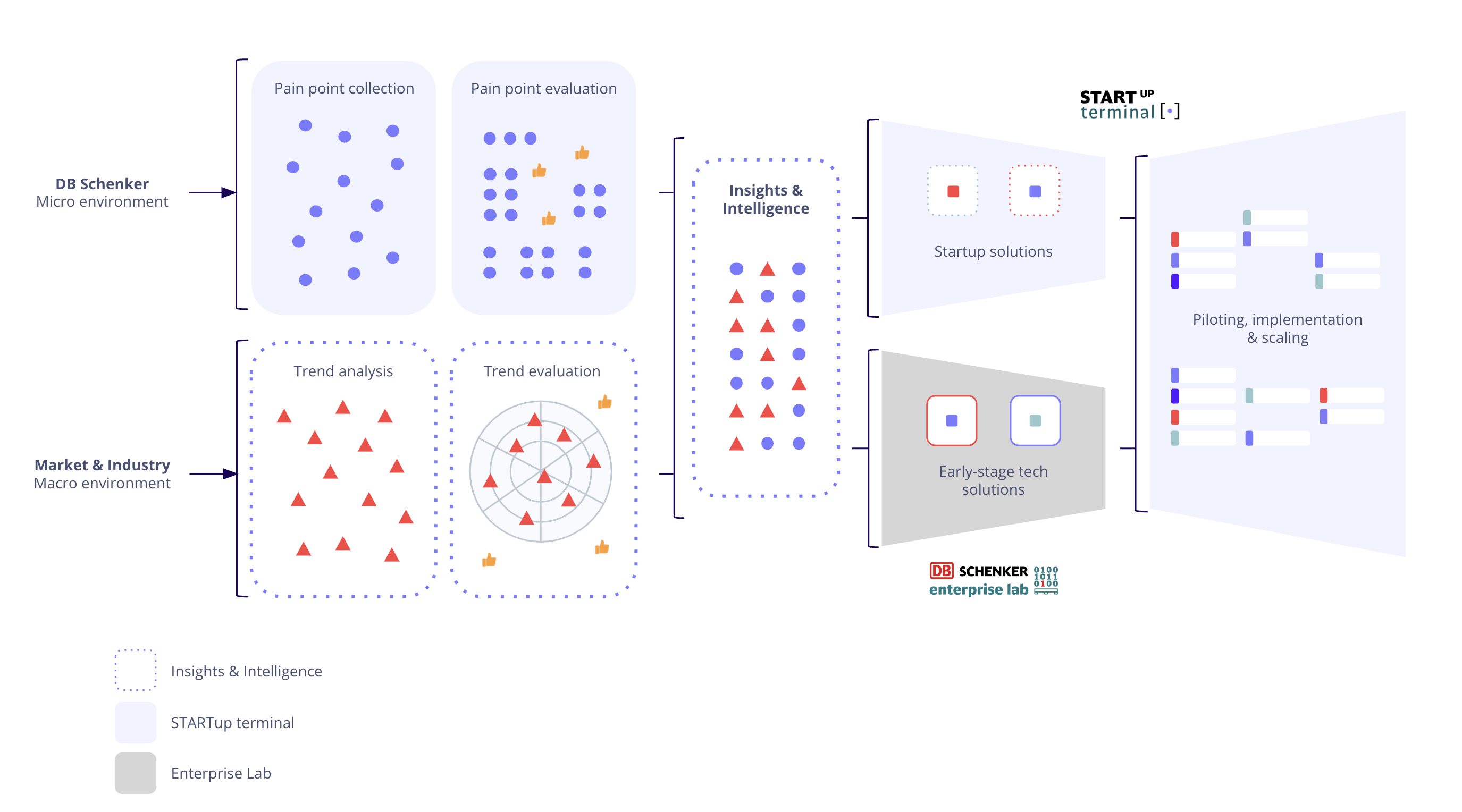
Another effective innovation strategy is combining customer pain point insights (micro signals) and trend analysis (macro signals). This process involves continuously monitoring both internal and external sources for signals of change. Once insights are identified, they guide the organization’s innovation priorities. We saw this process with DB Schenker - one of the world’s leading logistics service providers.
DB Schenker's innovation process is quite elaborate. Yet, before working with ITONICS, it managed its innovation activities with disparate tools: Jira for tracking startups, PowerPoint for trend analysis, and various project management applications. Teams, often working on interrelated yet distinct projects, struggled to align and share critical knowledge. With the STARTup terminal engaged in venture clienting, the Enterprise Lab exploring new tech solutions, and the Insights & Intelligence Team analyzing trends to guide the strategic focus across business units—DB Schenker needed one centralized tool to streamline the flow of innovation - and found it with ITONICS the Innovation OS.
NPD process example 3: R&D-driven product development
In industries such as healthcare, where safety and efficacy are critical, research and development (R&D) play a central role in the innovation process. The focus is on rigorous validation, ensuring that all new products or services meet high standards of quality and compliance. This approach requires close collaboration between R&D and marketing teams to ensure that innovations pass regulatory scrutiny and meet market demands. We saw the following innovation process at Merz - an internationally active, family-owned pharmaceutical company.
To determine the competitive landscape of the current portfolio, predefined search fields are used to collect knowledge from various sources:
-
Companies and their products as well as clinical trials, patents, publications
-
Internet searches, press releases, conferences, market reports
-
Employee contributions on specific topics, e.g. indications like Parkinson‘s disease or technologies like neurostimulation/-modulation devices
-
External experts who input data on emerging products and technologies
The collected insights are enriched by the AI-enabled signals feed, which automatically adds relevant market signals to the scouted products and companies. Other departments can additionally access, edit, and supplement the data. The most relevant products and companies are assigned to a specific technology field or indication and selected for further evaluation.
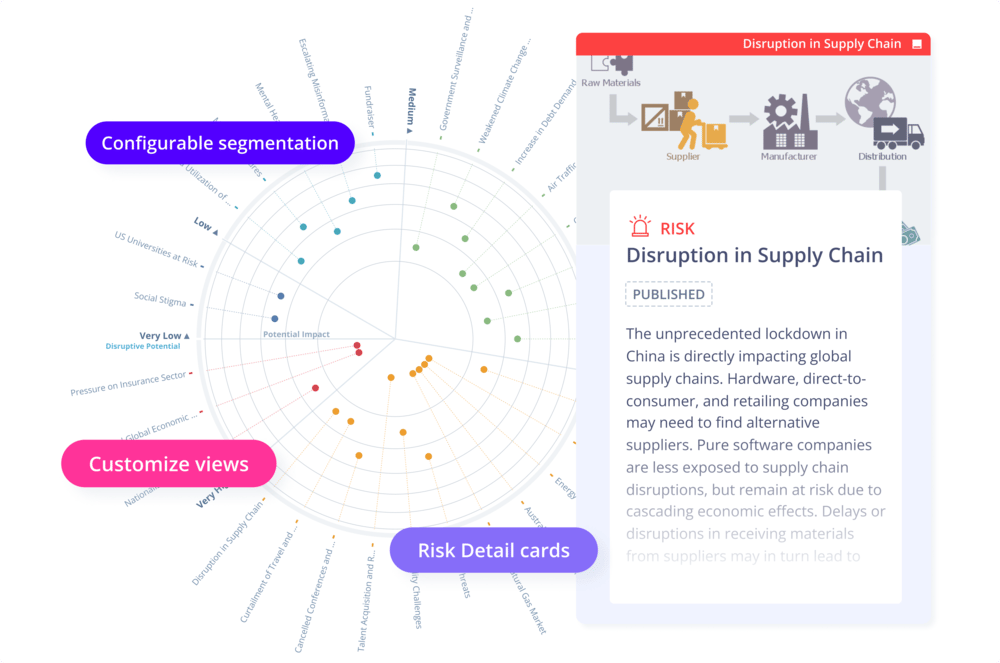
The hits are evaluated by the Scouting Team and experts from other departments. Evaluation criteria include, for example, the efficiency or the safety of a treatment. The evaluated results can be visualized in different Radars and provide the Screening Team and Business Development Board with evidence to make better strategic decisions on portfolio expansions.
The 4 different NPD strategies
New Product Development (NPD) strategies focus on the different NPD types and what can be new in a product. Each strategy reflects a different approach to how a product is changed or introduced to the market. Formulating an effective marketing strategy is crucial to reach target audiences and evaluate product performance.
Here are the four key NPD strategies (Exhibit 3):
Exhibit 3: New product development strategies
Improvement of existing features: This strategy involves refining or enhancing existing features of a product to make it more efficient or user-friendly. It’s about making incremental changes that add value to the current product line. Examples include software updates or enhancing product durability. This approach helps maintain customer interest and loyalty without major disruptions.
New design: Redesigning an existing product can refresh its market appeal and differentiate it from competitors. This strategy focuses on aesthetics, user experience, and ergonomic improvements. A new design can attract new customer segments and re-engage existing ones. Examples include updated smartphone models or reimagined car interiors that offer better comfort and style.
New function: This strategy introduces a new function to an existing product, broadening its use and appeal. Adding new capabilities, such as integrating smart technology into home appliances, transforms the product’s functionality while building on its core purpose. New functions can often shift a product’s position in the market from basic to premium.
Complete new system: A complete new system involves creating a product that is entirely new to the market, embodying breakthrough innovation. This can include disruptive technologies or concepts that redefine an industry. Examples include electric vehicles or smart home ecosystems. Such systems often target unmet needs and can position a company as a market leader.
These new product development strategies speak to one dimension of the famous Ansoff innovation matrix. The innovation matrix by Ansoff helps align NPD strategies with market perspectives by dividing product and market changes into four distinct categories.
Market penetration (existing product, existing market)
Strategies that involve improving existing features or new design changes fall here. The goal is to increase market share by making a product more appealing within the current market. Incremental enhancements can encourage repeat purchases and reinforce brand loyalty.
Product development (new product, existing market)
Introducing new functions or a complete redesign of a product fits into this category. This strategy aims to serve existing customers with a fresh or upgraded offering. Companies use this to differentiate their products and stand out in a competitive landscape.
Market development (existing product, new market)
Bringing an existing product with new design adaptations or added features into a new market segment fits here. This strategy helps companies explore new customer bases without creating an entirely new product. For example, expanding a popular software product to a different industry by tweaking its features for niche use cases.
Diversification (new product, new market)
A complete new system aligns with this strategy, where a company enters a new market with a groundbreaking product. This approach is high-risk but can yield significant rewards by tapping into uncharted territories. Examples include tech giants launching innovative platforms that create new categories, such as virtual reality systems.
Understanding the four NPD strategies and the context of Ansoff’s matrix helps companies choose the best approach for growth. It helps prioritize and build the right new product development portfolio. Whether through incremental improvements or radical innovation, aligning product development with the market perspective is key to a successful NPD process.
Common challenges to overcome in the new product development process
When a systematic new product development (NPD) process is not in place, companies face significant challenges that can hinder their innovation efforts and market success. A dedicated product development team, involving collaboration among technical engineers, finance teams, and market researchers, is crucial to ensure that products meet customer expectations and are financially viable. Here are four common challenges that arise:
Lack of Clear Direction and Prioritization
Without a structured process, teams may struggle to prioritize ideas and initiatives. This often results in scattered efforts, with resources being spread too thin across multiple projects. The absence of a clear roadmap can lead to confusion and stalled progress. To overcome this, companies need a systematic approach to prioritize projects based on market potential, feasibility, and alignment with business goals.
Ineffective Resource Allocation
When an NPD process is ad hoc or poorly defined, it’s difficult to allocate resources effectively. This can lead to overinvestment in unviable projects or underfunding promising ideas. Without a structured process, teams risk wasting time and budget on products that don’t reach the market or fail to meet customer needs. Establishing a defined process ensures that resources are channeled into the most promising projects, maximizing return on investment.
Develop a Clear Timeline
Missing product-market fit
A non-systematic approach often skips or minimizes crucial steps such as market research and customer validation. This can lead to products that miss the mark with consumers, either by not solving the right problems or lacking key features. To mitigate this, a structured NPD process should include thorough research and iterative feedback loops that align product development with real market needs.
Delays and Late Development Cycles
Without an organized process, the development cycle can become disjointed, leading to delays and inefficiencies. Teams may face communication gaps, redundant work, and missed deadlines. This lack of coordination can slow down time-to-market, giving competitors an edge. A systematic NPD process streamlines communication and workflow, enabling faster and more efficient product development.
Addressing these challenges involves implementing a structured NPD process that provides clarity, optimizes resources, incorporates customer insights, and ensures efficient development timelines.
New product development software and tools
New product development (NPD) software and tools play a crucial role in streamlining the process of bringing innovative products to market. These platforms are designed to facilitate every stage of the NPD process, from ideation to product launch, ensuring that teams work efficiently and collaboratively. Here’s an overview of the key features that leading NPD software typically offers:
1. Idea management and collaboration. Effective NPD tools provide robust idea management features, allowing teams to capture, organize, and evaluate new product ideas from various sources. Collaborative platforms enable cross-functional teams to contribute ideas, provide feedback, and refine concepts in real-time. This fosters an innovation-friendly environment where valuable insights can be shared easily, ensuring that only the most promising ideas move forward.
/Still%20images/Ideation%20Mockups%202025/ideation-organize-idea-flows-2025.webp?width=966&height=604&name=ideation-organize-idea-flows-2025.webp)
Exhibit 4: Ideation boards support effective idea management and collaboration
2. Trend and technology scouting. Staying ahead of market trends and emerging technologies is essential for successful NPD. Advanced software offers tools for trend and technology scouting, helping teams identify potential opportunities and threats. These features help companies understand market shifts and align their product strategies with evolving customer needs and industry trends.
3. Roadmapping and portfolio management. NPD software often includes comprehensive roadmapping capabilities to map out product development timelines and milestones. This allows companies to visualize the entire product lifecycle and strategically plan the steps needed to bring a product to market. Portfolio management features provide an overview of all ongoing projects, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and that the product pipeline aligns with company goals.
4. Workflow automation and process standardization. Standardizing the NPD process is key to reducing inefficiencies and improving productivity. NPD tools offer workflow automation to streamline repetitive tasks and establish consistent processes. This ensures that all teams follow the same procedures, minimizing miscommunication and project delays. Automation also reduces administrative burdens, allowing teams to focus on strategic activities.
5. Real-time data and performance tracking. Tracking progress and performance is crucial for any NPD initiative. High-quality software provides real-time dashboards and analytics that offer insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) such as time-to-market, resource use, and project milestones. This helps teams make data-driven decisions, adjust strategies as needed, and maintain alignment with business objectives.
6. Portals for customer feedback. To expand the pool of ideas and solutions, some NPD tools include external submission portals for crowdsourcing and partnerships. This feature supports open innovation by allowing companies to gather input from outside contributors, including startups, research institutions, and customers. It enables businesses to stay agile by integrating external perspectives and solutions into their product development efforts.
7. Compliance and risk management tools. Meeting regulatory standards and assessing risk are important aspects of NPD, especially in industries with strict compliance requirements. Leading software offers features for risk radars and compliance checks, helping teams identify potential issues early and stay within regulatory boundaries throughout the development process.
The combination of these features in NPD software empowers companies to streamline their innovation processes, reduce time-to-market, and ensure that new products meet customer needs. By integrating tools for idea management, trend scouting, roadmapping, and performance tracking, businesses can create a cohesive strategy that aligns teams and optimizes their NPD efforts.
Make new product development work with the right software
The ITONICS Innovation OS is the best new product development software to run a successful new product development process. At ITONICS, we understand the importance of innovation and NPD. We offer a comprehensive innovation management platform. Our Innovation OS embodies all the essentials of the best innovation management software and covers all the application areas in one tool. It will help you to:
-
Eliminate information silos: Dispersed teams and disconnected data often result in missed opportunities and duplicated efforts. With ITONICS, all your NPD projects, most innovative ideas, and market insights are centralized in one place. Create transparency and reduce inefficiencies by keeping everyone on the same page.
-
Streamline idea and feedback collection: Managing a high volume of ideas from various sources can be overwhelming. ITONICS allows you to capture, evaluate, and prioritize ideas from across the organization, including customers and partners, all in one structured process. This helps focus resources on the most impactful ideas and reduces time wasted on less promising ones.
-
Track NPD progress across teams: Monitoring the progress of multiple innovation projects across departments isn’t easy. ITONICS provides visual dashboards and roadmapping that give you a real-time overview of ongoing projects, ensuring you can quickly address roadblocks, identify risks, and keep everything on track.
-
Decrease product-market fit risks: By connecting new product development projects with trends, technologies, and customer feedback, ITONICS helps organizations align their new products with market developments and strategic objectives.
FAQs on new product development
What is new product development?
New product development (NPD) is the complete process of bringing a new product to market, from generating ideas to launching and managing the product post-launch. It involves market research, concept validation, prototyping, testing, and commercialization.
Why is new product development important for companies?
New product development helps companies stay competitive, enter new markets, and meet changing customer needs. A structured NPD approach increases the success rate of product launches, reduces risk, and ensures alignment with strategic business goals.
What are the key stages of the new product development process?
The standard stages in the NPD process include:
-
Idea generation
-
Idea screening
-
Concept development and testing
-
Business analysis
-
Product development
-
Market testing
-
Commercialization
How do companies generate new product ideas?
New product ideas can come from internal teams, customer feedback, trend scouting, startup collaborations, and competitor analysis. Many innovation-driven companies use platforms like ITONICS to structure and accelerate ideation and concept validation.
What tools support successful new product development?
Software tools like ITONICS supports the full NPD lifecycle, from idea capture and evaluation to prototyping, testing, and portfolio management. These tools improve transparency, collaboration, and time-to-market.

.webp?width=854&height=546&name=PostFinance_Innovation%20Process%20(1).webp)